Capsular Polysaccharide Is Essential for the Virulence of the Antimicrobial-Resistant Pathogen Enterobacter hormaechei
- PMID: 36779722
- PMCID: PMC10127600
- DOI: 10.1128/mbio.02590-22
Capsular Polysaccharide Is Essential for the Virulence of the Antimicrobial-Resistant Pathogen Enterobacter hormaechei
Abstract
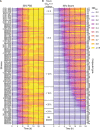
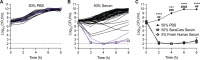
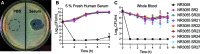
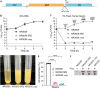
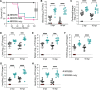
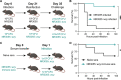
Nosocomial infections caused by multidrug-resistant (MDR) Enterobacter cloacae complex (ECC) pathogens are on the rise. However, the virulence strategies employed by these pathogens remain elusive. Here, we study the interaction of ECC clinical isolates with human serum to define how this pathogen evades the antimicrobial action of complement, one of the first lines of host-mediated immune defense. We identified a small number of serum-sensitive strains, including Enterobacter hormaechei strain NR3055, which we exploited for the in vitro selection of serum-resistant clones. Comparative genomics between the serum-sensitive NR3055 strain and the isolated serum-resistant clones revealed a premature stop codon in the wzy gene of the capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis locus of NR3055. The complementation of wzy conferred serum resistance to NR3055, prevented the deposition of complement proteins on the bacterial surface, inhibited phagocytosis by human neutrophils, and rendered the bacteria virulent in a mouse model of peritonitis. Mice exposed to a nonlethal dose of encapsulated NR3055 were protected from subsequent lethal infections by encapsulated NR3055, whereas mice that were previously exposed to unencapsulated NR3055 succumbed to infection. Thus, capsule is a key immune evasion determinant for E. hormaechei, and it is a potential target for prophylactics and therapeutics to combat these increasingly MDR human pathogens. IMPORTANCE Infections caused by antimicrobial resistant bacteria are of increasing concern, especially those due to carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae pathogens. Included in this group are species of the Enterobacter cloacae complex, regarding which there is a paucity of knowledge on the infection biology of the pathogens, despite their clinical relevance. In this study, we combine techniques in comparative genomics, bacterial genetics, and diverse models of infection to establish capsule as an important mechanism of Enterobacter pathogens to resist the antibacterial activity of serum, a first line of host defense against bacterial infections. We also show that immune memory targeting the Enterobacter capsule protects against lethal infection. The further characterization of Enterobacter infection biology and the immune response to infection are needed for the development of therapies and preventative interventions targeting these highly antibiotic resistant pathogens.
Keywords: Enterobacter; antimicrobial resistance; capsule; complement; pathogenesis; serum; serum resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Ludden C, Reuter S, Judge K, Gouliouris T, Blane B, Coll F, Naydenova P, Hunt M, Tracey A, Hopkins KL, Brown NM, Woodford N, Parkhill J, Peacock SJ. 2017. Sharing of carbapenemase-encoding plasmids between Enterobacteriaceae in UK sewage uncovered by MinION sequencing. Microb Genom 3:e000114. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000114. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

