Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 Lambda Variant Collected from a Child from Arkansas and Sequenced
- PMID: 36779742
- PMCID: PMC10019291
- DOI: 10.1128/mra.00007-23
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 Lambda Variant Collected from a Child from Arkansas and Sequenced
Abstract
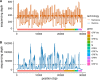
An eleven-year-old tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 Lambda variant. Sequencing was performed on the Oxford Nanopore and the Illumina NextSeq 500. Both platforms identified all 7 of the synonymous mutations in the sample, while all 28 nonsynonymous mutations were identified from Oxford Nanopore and 20 nonsynonymous mutations were identified from Illumina.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Quick J. 2020. nCoV-2019 sequencing protocol v3 (LoCost) V.3. https://www.protocols.io/view/ncov-2019-sequencing-protocol-v3-locost-bp.... Accessed August 2021.
-
- Loman N, Rowe W, Rambaut A. 2020. nCoV-2019 novel coronavirus bioinformatics protocol. https://artic.network/ncov-2019/ncov2019-bioinformatics-sop.html. Accessed August 2021.
-
- Li H. 2013. Aligning sequence reads, clone sequences and assembly contigs with BWA-MEM. arXiv 1303.3997v2 [q-bio.GN]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1303.3997.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous