PCSK6 and Survival in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
- PMID: 36780644
- PMCID: PMC10263132
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.202205-0845OC
PCSK6 and Survival in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Abstract
Rationale: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a devastating disease characterized by limited treatment options and high mortality. A better understanding of the molecular drivers of IPF progression is needed. Objectives: To identify and validate molecular determinants of IPF survival. Methods: A staged genome-wide association study was performed using paired genomic and survival data. Stage I cases were drawn from centers across the United States and Europe and stage II cases from Vanderbilt University. Cox proportional hazards regression was used to identify gene variants associated with differential transplantation-free survival (TFS). Stage I variants with nominal significance (P < 5 × 10-5) were advanced for stage II testing and meta-analyzed to identify those reaching genome-wide significance (P < 5 × 10-8). Downstream analyses were performed for genes and proteins associated with variants reaching genome-wide significance. Measurements and Main Results: After quality controls, 1,481 stage I cases and 397 stage II cases were included in the analysis. After filtering, 9,075,629 variants were tested in stage I, with 158 meeting advancement criteria. Four variants associated with TFS with consistent effect direction were identified in stage II, including one in an intron of PCSK6 (proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 6) reaching genome-wide significance (hazard ratio, 4.11 [95% confidence interval, 2.54-6.67]; P = 9.45 × 10-9). PCSK6 protein was highly expressed in IPF lung parenchyma. PCSK6 lung staining intensity, peripheral blood gene expression, and plasma concentration were associated with reduced TFS. Conclusions: We identified four novel variants associated with IPF survival, including one in PCSK6 that reached genome-wide significance. Downstream analyses suggested that PCSK6 protein plays a potentially important role in IPF progression.
Keywords: IPF; PCSK6 protein; genome-wide association study; genomics; survival.
Figures
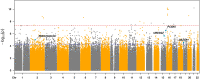
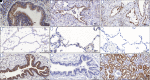


Comment in
-
Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 6: A Risk Factor for Survival in Pulmonary Fibrosis?Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2023 Jun 1;207(11):1421-1422. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202302-0266ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2023. PMID: 36812412 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
PCSK6: The Endogenous PAR-1 Agonist Driving Pulmonary Fibrosis?Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2023 Jun 15;207(12):1643-1644. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202303-0355LE. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2023. PMID: 36927336 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Raghu G, Remy-Jardin M, Myers JL, Richeldi L, Ryerson CJ, Lederer DJ, et al. American Thoracic Society, European Respiratory Society, Japanese Respiratory Society, and Latin American Thoracic Society Diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: an official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT clinical practice guideline. Am J Respir Crit Care Med . 2018;198:e44–e68. - PubMed
-
- Lederer DJ, Martinez FJ. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med . 2018;378:1811–1823. - PubMed
-
- Richeldi L, du Bois RM, Raghu G, Azuma A, Brown KK, Costabel U, et al. INPULSIS Trial Investigators Efficacy and safety of nintedanib in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med . 2014;370:2071–2082. - PubMed
-
- King TE, Jr, Bradford WZ, Castro-Bernardini S, Fagan EA, Glaspole I, Glassberg MK, et al. ASCEND Study Group A phase 3 trial of pirfenidone in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med . 2014;370:2083–2092. - PubMed
-
- Dempsey TM, Sangaralingham LR, Yao X, Sanghavi D, Shah ND, Limper AH. Clinical effectiveness of antifibrotic medications for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med . 2019;200:168–174. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 HL007605/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- 221680/Z/20/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 HL145372/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL130796/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 HL158935/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CDA 13-017/HX/HSRD VA/United States
- WT202849/Z/16/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- CS-2013-13-017/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- T32 HL007749/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 HL145266/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- NIHR201371/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- P01 HL092870/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/V00235X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- K23 HL146942/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RP-2017-08-ST2-014/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- UG3 HL145266/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- K23 HL138190/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL150301/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G0901226/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- I01 BX002378/BX/BLRD VA/United States

