Reduced secretion of LCN2 (lipocalin 2) from reactive astrocytes through autophagic and proteasomal regulation alleviates inflammatory stress and neuronal damage
- PMID: 36781380
- PMCID: PMC10351455
- DOI: 10.1080/15548627.2023.2180202
Reduced secretion of LCN2 (lipocalin 2) from reactive astrocytes through autophagic and proteasomal regulation alleviates inflammatory stress and neuronal damage
Abstract
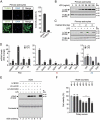
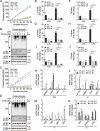
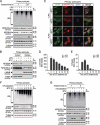
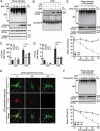
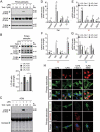
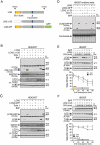
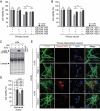
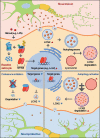
LCN2/neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin/24p3 (lipocalin 2) is a secretory protein that acts as a mammalian bacteriostatic molecule. Under neuroinflammatory stress conditions, LCN2 is produced and secreted by activated microglia and reactive astrocytes, resulting in neuronal apoptosis. However, it remains largely unknown whether inflammatory stress and neuronal loss can be minimized by modulating LCN2 production and secretion. Here, we first demonstrated that LCN2 was secreted from reactive astrocytes, which were stimulated by treatment with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) as an inflammatory stressor. Notably, we found two effective conditions that led to the reduction of induced LCN2 levels in reactive astrocytes: proteasome inhibition and macroautophagic/autophagic flux activation. Mechanistically, proteasome inhibition suppresses NFKB/NF-κB activation through NFKBIA/IκBα stabilization in primary astrocytes, even under inflammatory stress conditions, resulting in the downregulation of Lcn2 expression. In contrast, autophagic flux activation via MTOR inhibition reduced the intracellular levels of LCN2 through its pre-secretory degradation. In addition, we demonstrated that the N-terminal signal peptide of LCN2 is critical for its secretion and degradation, suggesting that these two pathways may be mechanistically coupled. Finally, we observed that LPS-induced and secreted LCN2 levels were reduced in the astrocyte-cultured medium under the above-mentioned conditions, resulting in increased neuronal viability, even under inflammatory stress.Abbreviations: ACM, astrocyte-conditioned medium; ALP, autophagy-lysosome pathway; BAF, bafilomycin A1; BTZ, bortezomib; CHX, cycloheximide; CNS, central nervous system; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein; GFP, green fluorescent protein; JAK, Janus kinase; KD, knockdown; LCN2, lipocalin 2; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; MACS, magnetic-activated cell sorting; MAP1LC3/LC3, microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3; MTOR, mechanistic target of rapamycin kinase; NFKB/NF-κB, nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B cells 1, p105; NFKBIA/IκBα, nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B cells inhibitor, alpha; OVEX, overexpression; SLC22A17, solute carrier family 22 member 17; SP, signal peptide; SQSTM1, sequestosome 1; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; TNF/TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor; TUBA, tubulin, alpha; TUBB3/β3-TUB, tubulin, beta 3 class III; UB, ubiquitin; UPS, ubiquitin-proteasome system.
Keywords: Autophagy; lipocalin 2 (LCN2); proteasome; protein degradation; reactive astrocyte; secretory protein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Neilands JB. Siderophores: structure and function of microbial iron transport compounds. J Biol Chem. 1995. Nov 10;270(45):26723–26726. - PubMed
-
- Yang J, Goetz D, Li JY, et al. An iron delivery pathway mediated by a lipocalin. Mol Cell. 2002. Nov;10(5):1045–1056. - PubMed
-
- Flo TH, Smith KD, Sato S, et al. Lipocalin 2 mediates an innate immune response to bacterial infection by sequestrating iron. Nature. 2004. Dec 16;432(7019):917–921. - PubMed
-
- Kjeldsen L, Johnsen AH, Sengelov H, et al. Isolation and primary structure of NGAL, a novel protein associated with human neutrophil gelatinase. J Biol Chem. 1993. May 15;268(14):10425–10432. - PubMed
-
- Goetz DH, Willie ST, Armen RS, et al. Ligand preference inferred from the structure of neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin. Biochemistry. 2000. Feb 29;39(8):1935–1941. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
