Content Validity and Cognitive Debriefing of a Patient-Reported Outcome Instrument Evaluating Symptoms and Disease Impact in Patients with Geographic Atrophy
- PMID: 36781630
- PMCID: PMC10011295
- DOI: 10.1007/s40123-023-00667-3
Content Validity and Cognitive Debriefing of a Patient-Reported Outcome Instrument Evaluating Symptoms and Disease Impact in Patients with Geographic Atrophy
Abstract
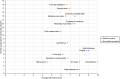
Introduction: Geographic atrophy (GA) occurs in the later stages of dry age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and impairs visual acuity, eventually causing permanent blindness in some patients and impacting patient quality of life. Patient-reported outcome (PRO) measures that assess the experience of patients with visual impairment do not sufficiently capture all concepts salient to patients with GA. In this study the experience of patients with GA secondary to dry AMD was evaluated, and items from the novel 10-item Visual Impairment Symptom Severity Assessment (VISSA-10) PRO instrument were mapped to salient symptoms to assess its content validity, ease of use, and relevance.
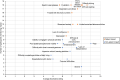
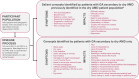
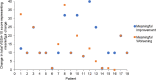
Methods: Concept elicitation interviews were conducted with patients with GA to determine salient symptoms and impacts of GA, and a conceptual model was developed to reflect these. The items in the VISSA-10 instrument were then mapped onto the salient symptoms included in this conceptual model. Cognitive debriefing interviews were also conducted with the same cohort to determine the comprehensiveness and comprehensibility of the instrument, and to qualitatively assess levels of change considered meaningful by patients.
Results: In total, 25 symptoms and 36 impacts were reported by 19 patients with GA, with seven symptoms and 11 impacts identified as salient. Of these, 12 symptoms and 15 impacts reported were not included in a previously published conceptual model for patients with dry AMD. Overall, eight of the ten items from the VISSA-10 instrument mapped to salient symptoms reported by patients with GA. All patients reported that the instrument was clear and easy to understand.
Conclusions: The VISSA-10 instrument was shown to be content valid, clear, and comprehensible, with sufficient concept coverage to measure the experience of patients with GA. Although further quantitative validation is required, this instrument has demonstrated potential for implementation in future clinical trials to evaluate the efficacy of new treatments for GA.
Keywords: Clinical outcomes assessment; Cognitive debriefing; Content validity; Geographic atrophy; Patient-reported outcomes; Vision; Visual acuity.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

