Conduction system pacing: promoting the physiology to prevent heart failure
- PMID: 36781809
- PMCID: PMC9941252
- DOI: 10.1007/s10741-023-10296-4
Conduction system pacing: promoting the physiology to prevent heart failure
Abstract
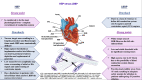
Cardiac conduction system pacing provides physiological ventricular activation by directly stimulating the conduction system. This review describes the two types of conduction system pacing: His bundle pacing (HBP) and left bundle area pacing (LBAP). The most significant advantage of HB pacing is that it can provide a regular, narrow QRS; however, the disadvantages are challenging implantation and a high risk of re-intervention due to lead dislodgement and the development of high pacing threshold. LBAP provides optimum physiological activation of the left ventricle by engaging the left bundle/fascicular fibers. LBAP is more physiological than traditional RV apical pacing and could be an attractive alternative to conventional cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT). The advantages of LBAP are a relatively more straightforward implantation technique than HBP, better lead stability and pacing thresholds. HBP and LBAP are more physiological than right ventricular pacing and may be used instead of conventional pacemakers. Both HBP and LBBP are being investigated as alternatives to conventional CRT.
Keywords: Cardiac resynchronization; Heart failure; His bundle pacing; Left bundle area pacing.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Arora V, Suri P. Physiological pacing: a new road to future. Indian J Clin Cardiol. 2021;2(1):32–43. doi: 10.1177/2632463620978045. - DOI
-
- Vijayaraman P, Dandamudi G (2016) Anatomical approach to permanent His bundle pacing: optimizing His bundle capture. J Electrocardiol 49(5):649–57.10.1016/j.jelectrocard.2016.07.003 - PubMed
-
- Ponnusamy SS. A road to physiological pacing. Indian J Clin Cardiol. 2021;2(1):7–9. doi: 10.1177/26324636211001585. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous