ANGPTL4 stabilizes atherosclerotic plaques and modulates the phenotypic transition of vascular smooth muscle cells through KLF4 downregulation
- PMID: 36782020
- PMCID: PMC9981608
- DOI: 10.1038/s12276-023-00937-x
ANGPTL4 stabilizes atherosclerotic plaques and modulates the phenotypic transition of vascular smooth muscle cells through KLF4 downregulation
Abstract
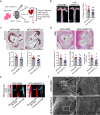
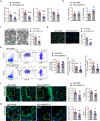
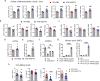
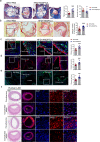
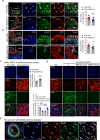
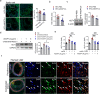
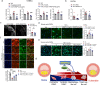
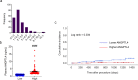
Atherosclerosis, the leading cause of death, is a vascular disease of chronic inflammation. We recently showed that angiopoietin-like 4 (ANGPTL4) promotes cardiac repair by suppressing pathological inflammation. Given the fundamental contribution of inflammation to atherosclerosis, we assessed the role of ANGPTL4 in the development of atherosclerosis and determined whether ANGPTL4 regulates atherosclerotic plaque stability. We injected ANGPTL4 protein twice a week into atherosclerotic Apoe-/- mice and analyzed the atherosclerotic lesion size, inflammation, and plaque stability. In atherosclerotic mice, ANGPTL4 reduced atherosclerotic plaque size and vascular inflammation. In the atherosclerotic lesions and fibrous caps, the number of α-SMA(+), SM22α(+), and SM-MHC(+) cells was higher, while the number of CD68(+) and Mac2(+) cells was lower in the ANGPTL4 group. Most importantly, the fibrous cap was significantly thicker in the ANGPTL4 group than in the control group. Smooth muscle cells (SMCs) isolated from atherosclerotic aortas showed significantly increased expression of CD68 and Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4), a modulator of the vascular SMC phenotype, along with downregulation of α-SMA, and these changes were attenuated by ANGPTL4 treatment. Furthermore, ANGPTL4 reduced TNFα-induced NADPH oxidase 1 (NOX1), a major source of reactive oxygen species, resulting in the attenuation of KLF4-mediated SMC phenotypic changes. We showed that acute myocardial infarction (AMI) patients with higher levels of ANGPTL4 had fewer vascular events than AMI patients with lower levels of ANGPTL4 (p < 0.05). Our results reveal that ANGPTL4 treatment inhibits atherogenesis and suggest that targeting vascular stability and inflammation may serve as a novel therapeutic strategy to prevent and treat atherosclerosis. Even more importantly, ANGPTL4 treatment inhibited the phenotypic changes of SMCs into macrophage-like cells by downregulating NOX1 activation of KLF4, leading to the formation of more stable plaques.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Stress, Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotype and Atherosclerosis: Novel Insight into Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotypic Transition in Atherosclerosis.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2024 Aug;26(8):411-425. doi: 10.1007/s11883-024-01220-8. Epub 2024 May 30. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2024. PMID: 38814419 Review.
-
Melatonin Ameliorates Atherosclerotic Plaque Vulnerability by Regulating PPARδ-Associated Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotypic Switching.J Pineal Res. 2024 Aug;76(5):e12988. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12988. J Pineal Res. 2024. PMID: 38982751
-
NOXA1-dependent NADPH oxidase regulates redox signaling and phenotype of vascular smooth muscle cell during atherogenesis.Redox Biol. 2019 Feb;21:101063. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2018.11.021. Epub 2018 Nov 29. Redox Biol. 2019. PMID: 30576919 Free PMC article.
-
AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Alpha 2 Deletion Induces VSMC Phenotypic Switching and Reduces Features of Atherosclerotic Plaque Stability.Circ Res. 2016 Sep 2;119(6):718-30. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.308689. Epub 2016 Jul 20. Circ Res. 2016. PMID: 27439892 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNAs at the crossroad of vascular smooth muscle cell phenotypic modulation in atherosclerosis and neointimal formation.Atherosclerosis. 2023 Jun;374:34-43. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2022.11.021. Epub 2022 Dec 6. Atherosclerosis. 2023. PMID: 36513554 Review.
Cited by
-
ANGPTL4-the Link Binding Lipid Metabolism and Inflammation.Curr Med Chem. 2025;32(15):2931-2949. doi: 10.2174/0109298673320024240829070906. Curr Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39252623 Review.
-
Epsins oversee smooth muscle cell reprograming by influencing master regulators KLF4 and OCT4.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 26:2024.01.08.574714. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.08.574714. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39131381 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Chronotherapy involving rosiglitazone regulates the phenotypic switch of vascular smooth muscle cells by shifting the phase of TNF-α rhythm through triglyceride accumulation in macrophages.Heliyon. 2024 May 16;10(10):e30708. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30708. eCollection 2024 May 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38803898 Free PMC article.
-
Stress, Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotype and Atherosclerosis: Novel Insight into Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotypic Transition in Atherosclerosis.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2024 Aug;26(8):411-425. doi: 10.1007/s11883-024-01220-8. Epub 2024 May 30. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2024. PMID: 38814419 Review.
-
Understanding genomic medicine for thoracic aortic disease through the lens of induced pluripotent stem cells.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Feb 19;11:1349548. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1349548. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 38440211 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

