Atypical functions of xenobiotic receptors in lipid and glucose metabolism
- PMID: 36785576
- PMCID: PMC9912049
- DOI: 10.1515/mr-2022-0032
Atypical functions of xenobiotic receptors in lipid and glucose metabolism
Abstract
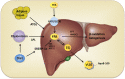
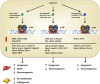
Xenobiotic receptors are traditionally defined as xenobiotic chemical-sensing receptors, the activation of which transcriptionally regulates the expression of enzymes and transporters involved in the metabolism and disposition of xenobiotics. Emerging evidence suggests that "xenobiotic receptors" also have diverse endobiotic functions, including their effects on lipid metabolism and energy metabolism. Dyslipidemia is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease, diabetes, obesity, metabolic syndrome, stroke, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Understanding the molecular mechanism by which transcriptional factors, including the xenobiotic receptors, regulate lipid homeostasis will help to develop preventive and therapeutic approaches. This review describes recent advances in our understanding the atypical roles of three xenobiotic receptors: aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR), pregnane X receptor (PXR), and constitutive androstane receptor (CAR), in metabolic disorders, with a particular focus on their effects on lipid and glucose metabolism. Collectively, the literatures suggest the potential values of AhR, PXR and CAR as therapeutic targets for the treatment of NAFLD, NASH, obesity and diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: aryl hydrocarbon receptor; constitutive androstane receptor; lipid metabolism; pregnane X receptor; xenobiotic receptors.
© 2022 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Kochanek KD, Murphy SL, Anderson RN, Scott C. Deaths: final data for 2002. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2004;53:1–115. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
