Monkeypox: a model-free analysis
- PMID: 36785810
- PMCID: PMC9908498
- DOI: 10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-03709-8
Monkeypox: a model-free analysis
Abstract
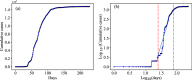
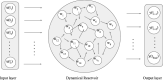
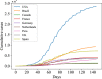
Monkeypox is a zoonotic disease caused by a virus that is a member of the orthopox genus, which has been causing an outbreak since May 2022 around the globe outside of its country of origin Democratic Republic of the Congo, Africa. Here we systematically analyze the data of cumulative infection per day adapting model-free analysis, in particular, statistically using the power law distribution, and then separately we use reservoir computing-based Echo state network (ESN) to predict and forecast the disease spread. We also use the power law to characterize the country-specific infection rate which will characterize the growth pattern of the disease spread such as whether the disease spread reached a saturation state or not. The results obtained from power law method were then compared with the outbreak of the smallpox virus in 1907 in Tokyo, Japan. The results from the machine learning-based method are also validated by the power law scaling exponent, and the correlation has been reported.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Società Italiana di Fisica and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2023, Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
