A novel firefly algorithm approach for efficient feature selection with COVID-19 dataset
- PMID: 36785847
- PMCID: PMC9901218
- DOI: 10.1016/j.micpro.2023.104778
A novel firefly algorithm approach for efficient feature selection with COVID-19 dataset
Abstract
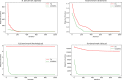
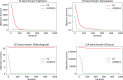
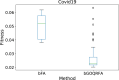
Feature selection is one of the most important challenges in machine learning and data science. This process is usually performed in the data preprocessing phase, where the data is transformed to a proper format for further operations by machine learning algorithm. Many real-world datasets are highly dimensional with many irrelevant, even redundant features. These kinds of features do not improve classification accuracy and can even shrink down performance of a classifier. The goal of feature selection is to find optimal (or sub-optimal) subset of features that contain relevant information about the dataset from which machine learning algorithms can derive useful conclusions. In this manuscript, a novel version of firefly algorithm (FA) is proposed and adapted for feature selection challenge. Proposed method significantly improves performance of the basic FA, and also outperforms other state-of-the-art metaheuristics for both, benchmark bound-constrained and practical feature selection tasks. Method was first validated on standard unconstrained benchmarks and later it was applied for feature selection by using 21 standard University of California, Irvine (UCL) datasets. Moreover, presented approach was also tested for relatively novel COVID-19 dataset for predicting patients health, and one microcontroller microarray dataset. Results obtained in all practical simulations attest robustness and efficiency of proposed algorithm in terms of convergence, solutions' quality and classification accuracy. More precisely, the proposed approach obtained the best classification accuracy on 13 out of 21 total datasets, significantly outperforming other competitor methods.
Keywords: COVID-19 dataset; Feature selection; Firefly algorithm; Genetic operators; Quasi-reflection-based learning; Swarm intelligence.
© 2023 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Quasi-reflection learning arithmetic optimization algorithm firefly search for feature selection.Heliyon. 2023 Apr 6;9(4):e15378. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15378. eCollection 2023 Apr. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37101631 Free PMC article.
-
An Innovative Excited-ACS-IDGWO Algorithm for Optimal Biomedical Data Feature Selection.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Aug 17;2020:8506365. doi: 10.1155/2020/8506365. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32908920 Free PMC article.
-
Novel chaotic oppositional fruit fly optimization algorithm for feature selection applied on COVID 19 patients' health prediction.PLoS One. 2022 Oct 10;17(10):e0275727. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0275727. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36215218 Free PMC article.
-
Feature Selection Problem and Metaheuristics: A Systematic Literature Review about Its Formulation, Evaluation and Applications.Biomimetics (Basel). 2023 Dec 25;9(1):9. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics9010009. Biomimetics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38248583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A new feature selection approach with binary exponential henry gas solubility optimization and hybrid data transformation methods.MethodsX. 2024 May 20;12:102770. doi: 10.1016/j.mex.2024.102770. eCollection 2024 Jun. MethodsX. 2024. PMID: 39677828 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An optimal neural network to design generators and stabilizers for multi-machine power systems based on a promoted firefly algorithm.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):21663. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05547-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40596328 Free PMC article.
-
An Explainable LSTM-Based Intrusion Detection System Optimized by Firefly Algorithm for IoT Networks.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Apr 4;25(7):2288. doi: 10.3390/s25072288. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40218800 Free PMC article.
-
Concordance and generalization of an AI algorithm with real-world clinical data in the pre-omicron and omicron era.Heliyon. 2024 Feb 2;10(3):e25410. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25410. eCollection 2024 Feb 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38356547 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-feature fusion and dandelion optimizer based model for automatically diagnosing the gastrointestinal diseases.PeerJ Comput Sci. 2024 Feb 28;10:e1919. doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.1919. eCollection 2024. PeerJ Comput Sci. 2024. PMID: 38435605 Free PMC article.
-
A BiLSTM model enhanced with multi-objective arithmetic optimization for COVID-19 diagnosis from CT images.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 29;15(1):10841. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-94654-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40155431 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Luo S., Cheng L., Ren B. Practical swarm optimization based fault-tolerance algorithm for the Internet of Things. KSII Trans. Internet Inf. Syst. (TIIS) 2014;8(3):735–748.
-
- Wu Q., Ding G., Xu Y., Feng S., Du Z., Wang J., Long K. Cognitive Internet of Things: A new paradigm beyond connection. IEEE Internet Things J. 2014;1(2):129–143. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2014.2311513. - DOI
-
- Messaoud S., Bradai A., Bukhari S.H.R., Quang P.T.A., Ahmed O.B., Atri M. A survey on machine learning in Internet of Things: Algorithms, strategies, and applications. Internet Things. 2020;12 doi: 10.1016/j.iot.2020.100314. URL https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2542660520301451. - DOI
-
- Zenggang X., Mingyang Z., Xuemin Z., Sanyuan Z., Fang X., Xiaochao Z., Yunyun W., Xiang L. Social similarity routing algorithm based on socially aware networks in the big data environment. J. Signal Process. Syst. 2022;94(11):1253–1267.
-
- Chandrashekar G., Sahin F. A survey on feature selection methods. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2014;40(1):16–28. doi: 10.1016/j.compeleceng.2013.11.024. URL https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0045790613003066, 40th-year commemorative issue. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
