Safety of biological and targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs for rheumatoid arthritis as used in clinical practice: results from the ARTIS programme
- PMID: 36787994
- PMCID: PMC10176333
- DOI: 10.1136/ard-2022-223762
Safety of biological and targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs for rheumatoid arthritis as used in clinical practice: results from the ARTIS programme
Abstract
Objective: Longitudinal clinical registry-infrastructures such as Anti-Rheumatic Therapies in Sweden (ARTIS) allow simultaneous comparison of the safety of individual immunomodulatory drugs used in clinical practice, with consistent definitions of treatment cohorts, follow-up and outcomes. Our objective was to assess and compare incidence rates of key safety outcomes for individual targeted synthetic or biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (b/ts DMARDs) in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), updating previous reports and including newer treatments including Janus Kinase inhibitors (JAKi).
Methods: Nationwide register-based cohort study including all patients with RA in Sweden registered as starting any b/tsDMARD 1 January 2010 through 31 December 2020, followed until 30 June 2021 (N=20 117). The incidence rates of selected outcomes, identified through national healthcare registers, were compared between individual b/tsDMARDs, adjusted for confounding by demographics, RA disease characteristics and comorbidity.
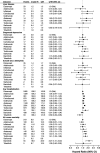
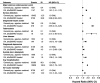
Results: There were marked differences in treatment discontinuations due to adverse events (rates per 1000 person-years ranged from 18 on rituximab to 57 on tofacitinib), but few significant differences were observed for the serious adverse events under study. Neither cardiovascular events nor general serious infections were more frequent on baricitinib or tofacitinib versus bDMARDs, but JAKi were associated with higher rates of hospital-treated herpes zoster (HR vs etanercept, 3.82 (95% CI 2.05 to 7.09) and 4.00 (1.59 to 10.06)). Low number of events limited some comparisons, in particular for sarilumab and tofacitinib.
Conclusion: Data from ARTIS supports that the b/tsDMARDs currently used to treat RA have acceptable and largely similar safety profiles, but differences exist in particular concerning tolerability and specific infection risks.
Keywords: Antirheumatic Agents; Arthritis, Rheumatoid; Biological Therapy; Cardiovascular Diseases; Epidemiology.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The ARTIS project is supported by agreements between Karolinska Institutet (with JA as PI) and the listed entities, mainly for the national safety monitoring of rheumatology immunomodulators in Sweden (ARTIS): Abbvie, BMS, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, MSD, Pfizer, Roche, Samsung Bioepis, Sanofi. TF, HB, DDG and BD are partly employed by the ARTIS project. EL, MM, NF, UL and HFdE report no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Bergstra SA, Sepriano A, Kerschbaumer A, et al. . Efficacy, duration of use and safety of glucocorticoids: a systematic literature review Informing the 2022 update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2023;82:81–94. 10.1136/ard-2022-223358 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kurz X, Perez-Gutthann S, ENCePP Steering Group . Strengthening Standards, transparency, and collaboration to support medicine evaluation: ten years of the European network of centres for pharmacoepidemiology and pharmacovigilance (encepp). Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf 2018;27:245–52. 10.1002/pds.4381 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

