Polyarteritis Nodosa Following mRNA-1273 COVID-19 Vaccination: Case Study and Review of Immunological Mechanisms
- PMID: 36788908
- PMCID: PMC9911313
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.33620
Polyarteritis Nodosa Following mRNA-1273 COVID-19 Vaccination: Case Study and Review of Immunological Mechanisms
Abstract
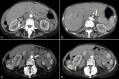
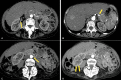
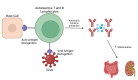
Numerous post-vaccine complications have been reported secondary to the COVID-19 vaccine. Many of these complications are believed to be due to a hyperactive immune system. A 59-year-old woman developed diffuse abdominal pain two days after receiving the mRNA-1273 COVID-19 vaccine (Moderna). A computerized tomography (CT) angiogram of the abdomen and pelvis revealed the presence of numerous vascular irregularities in the celiac axis, bilateral renal arteries, and inferior mesenteric artery consistent with polyarteritis nodosa (PAN), a medium-vessel vasculitis. The patient was managed with intravenous methylprednisolone 500 mg daily for three days and was then placed on oral methotrexate (MTX) 12.5 mg daily for immunosuppressive maintenance treatment. Until now, a limited number of cases of polyarteritis nodosa secondary to the COVID-19 vaccine have been reported. Major mechanisms of post-vaccine autoimmunity are molecular mimicry and autoantibody production. Although rare adverse events from COVID-19 vaccination are possible, there remains an immense benefit to vaccination in preventing COVID-19-related morbidity and mortality.
Keywords: coronavirus disease 2019; covid 19; moderna covid-19 vaccine; moderna mrna adverse effects; mrna-1273 vaccine; pfizer-biontech covid-19 vaccine; pfizer-biontech covid-19 vaccine related adverse events; polyarteritis nodosa; sars-cov-2; severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
Copyright © 2023, Srichawla et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
COVID-19 vaccines: comparison of biological, pharmacological characteristics and adverse effects of Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna Vaccines.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021 Feb;25(3):1663-1669. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202102_24877. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33629336 Review.
-
Possible case of polyarteritis nodosa with epididymitis following COVID-19 vaccination: A case report and review of the literature.Mod Rheumatol Case Rep. 2023 Jan 3;7(1):172-176. doi: 10.1093/mrcr/rxac085. Mod Rheumatol Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 36305628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of COVID-19 Vaccines After Reports of Adverse Events Among Adult Recipients of Janssen (Johnson & Johnson) and mRNA COVID-19 Vaccines (Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna): Update from the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices - United States, July 2021.MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021 Aug 13;70(32):1094-1099. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7032e4. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021. PMID: 34383735 Free PMC article.
-
Association between history of SARS-CoV-2 infection and severe systemic adverse events after mRNA COVID-19 vaccination among U.S. adults.Vaccine. 2022 Dec 12;40(52):7653-7659. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2022.10.073. Epub 2022 Nov 1. Vaccine. 2022. PMID: 36372665 Free PMC article.
-
ANCA-Associated Vasculitis Following Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine.Am J Kidney Dis. 2021 Oct;78(4):611-613. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2021.06.016. Epub 2021 Jul 17. Am J Kidney Dis. 2021. PMID: 34280507 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
New-Onset Rheumatic Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases Following SARS-CoV-2 Vaccinations until May 2023: A Systematic Review.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Oct 8;11(10):1571. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11101571. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37896974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post COVID-19 vaccination medium vessel vasculitis: a systematic review of case reports.Infection. 2024 Aug;52(4):1207-1213. doi: 10.1007/s15010-024-02217-w. Epub 2024 Mar 14. Infection. 2024. PMID: 38483787
References
-
- Clinical approach to diagnosis and therapy of polyarteritis nodosa. Hočevar A, Tomšič M, Perdan Pirkmajer K. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2021;23:14. - PubMed
-
- Gastrointestinal involvement in polyarteritis nodosa. Ebert EC, Hagspiel KD, Nagar M, Schlesinger N. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;6:960–966. - PubMed
-
- Diagnosis and classification of polyarteritis nodosa. Hernández-Rodríguez J, Alba MA, Prieto-González S, Cid MC. J Autoimmun. 2014;48-49:84–89. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
