Polyarteritis Nodosa Following mRNA-1273 COVID-19 Vaccination: Case Study and Review of Immunological Mechanisms
- PMID: 36788908
- PMCID: PMC9911313
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.33620
Polyarteritis Nodosa Following mRNA-1273 COVID-19 Vaccination: Case Study and Review of Immunological Mechanisms
Abstract
Numerous post-vaccine complications have been reported secondary to the COVID-19 vaccine. Many of these complications are believed to be due to a hyperactive immune system. A 59-year-old woman developed diffuse abdominal pain two days after receiving the mRNA-1273 COVID-19 vaccine (Moderna). A computerized tomography (CT) angiogram of the abdomen and pelvis revealed the presence of numerous vascular irregularities in the celiac axis, bilateral renal arteries, and inferior mesenteric artery consistent with polyarteritis nodosa (PAN), a medium-vessel vasculitis. The patient was managed with intravenous methylprednisolone 500 mg daily for three days and was then placed on oral methotrexate (MTX) 12.5 mg daily for immunosuppressive maintenance treatment. Until now, a limited number of cases of polyarteritis nodosa secondary to the COVID-19 vaccine have been reported. Major mechanisms of post-vaccine autoimmunity are molecular mimicry and autoantibody production. Although rare adverse events from COVID-19 vaccination are possible, there remains an immense benefit to vaccination in preventing COVID-19-related morbidity and mortality.
Keywords: coronavirus disease 2019; covid 19; moderna covid-19 vaccine; moderna mrna adverse effects; mrna-1273 vaccine; pfizer-biontech covid-19 vaccine; pfizer-biontech covid-19 vaccine related adverse events; polyarteritis nodosa; sars-cov-2; severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
Copyright © 2023, Srichawla et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
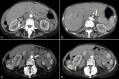
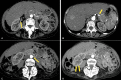
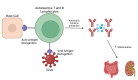
References
-
- Clinical approach to diagnosis and therapy of polyarteritis nodosa. Hočevar A, Tomšič M, Perdan Pirkmajer K. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2021;23:14. - PubMed
-
- Gastrointestinal involvement in polyarteritis nodosa. Ebert EC, Hagspiel KD, Nagar M, Schlesinger N. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;6:960–966. - PubMed
-
- Diagnosis and classification of polyarteritis nodosa. Hernández-Rodríguez J, Alba MA, Prieto-González S, Cid MC. J Autoimmun. 2014;48-49:84–89. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
