Risk factors and a prediction model for sepsis: A multicenter retrospective study in China
- PMID: 36789021
- PMCID: PMC9924017
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jointm.2022.02.004
Risk factors and a prediction model for sepsis: A multicenter retrospective study in China
Abstract
Background: Sepsis is typically associated with poor outcomes. There are various risk factors and predictive models for sepsis based on clinical indicators. However, these models are usually predictive of all critical patients. This study explored the risk factors for 28-day outcomes of patients with sepsis and developed a prognosis prediction model.
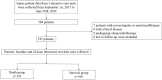
Methods: This was a multicenter retrospective analysis of sepsis patients hospitalized in three intensive care units (ICUs) from September 1st 2015, to June 30th 2020. Demographic, clinical history, and laboratory test data were extracted from patient records. Investigators explored the risk factors affecting 28-day sepsis prognosis by univariate analysis. The effects of confounding factors were excluded by multivariate logistic regression analysis, and new joint predictive factors were calculated. A model predicting 28-day sepsis prognosis was constructed through data processing analysis.
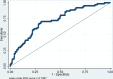
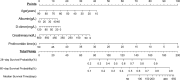
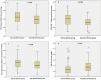
Results: A total of 545 patients with sepsis were included. The 28-day mortality rate was 32.3%. Risk factors including age, D-dimer, albumin, creatinine, and prothrombin time (PT) were predictive of death from sepsis. The goodness-of-fit value for this prediction model was 0.534, and the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve was 0.7207. Further analysis of the immune subgroups (n=140) revealed a significant decrease in CD3+, CD4+CD8-, and CD4+CD29+ memory effector T lymphocytes and an increase in CD56+ natural killer (NK) cells in the hypoalbuminemia group compared with the normal albumin group (65.5 vs. 58.3, P=0.005; 41.2 vs. 32.4, P=0.005; 21.8 vs. 17.1, P=0.029; 12.6 vs. 17.6, P=0.004).
Conclusions: Risk factors for 28-day sepsis mortality include age, D-dimer, creatinine, PT, and albumin. A decrease in albumin level may exacerbate immunosuppression in patients with sepsis. This study establishes a prediction model based on these indicators, which shows a good degree of calibration and differentiation. This model may provide good predictive value for clinical sepsis prognosis.
Keywords: Hypoalbuminemia; Immunosuppression; Model; Risk factors; Sepsis.
© 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of Chinese Medical Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

