Therapeutic efficacy of spirulina against ovalbumin and cigarette smoke-induced asthma-specific stress biomarkers in Sprague-Dawley rats
- PMID: 36789047
- PMCID: PMC9922124
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.3132
Therapeutic efficacy of spirulina against ovalbumin and cigarette smoke-induced asthma-specific stress biomarkers in Sprague-Dawley rats
Abstract
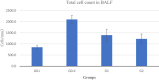
Due to the high prevalence of allergies and asthma, awareness about allergens and therapeutic use of functional foods and nutraceuticals have gained immense attention. Spirulina powder is being used as health-boosting and antioxidant agent against several ailments owing to its unique nutritional profile. Considering its antioxidant role, the current study was focused on exploring therapeutic role of spirulina against stress biomarkers in asthmatic model. To assess the therapeutic efficacy of spirulina against allergic asthma-specific oxidative stress biomarkers, a model feed trial was conducted and rats were divided into four groups (n = 10). G0-I (negative control), G0-II (positive control), whereas GI (spirulina) and G2 (salbutamol) served as treatment groups. Salbutamol is a chemical compound which is used in several antiallergic medicines because it works as bronchodilator. G2 group was given salbutamol for comparison of results. For asthma induction, rats were given intraperitoneal injection of ovalbumin on 7th, 14th, and 21st day. Treatment groups were given spirulina powder (500 mg/kg body weight) and salbutamol (1 mg/kg), respectively, after the induction of asthma. All three asthmatic groups were also exposed to cigarette smoke daily along with respective treatment for 4 weeks. Asthma induction caused an increase in total cell count in bronchioalveolar fluid (BALF), while spirulina treatment reduced total cells in BALF by 33.50% and salbutamol by 41.7%. Level of interleukins (IL) like IL-4 decreased by 33.32% & 48.56% in G1 and G2. Similarly, IL-5 and IL-13 levels reduced by 40.9% & 49.9% and 18.62% & 38.02%, respectively, in G1 and G2. Serum levels of Immunoglobin-E (Ig-E) declined by 29.70% and 52.82%, while histamine levels were 26.23% & 45.58% less at the end of study in comparison to positive control. Moreover, histological analysis of lung tissue revealed that both spirulina and salbutamol effectively reduced ovalbumin and cigarette smoke-induced moderate to severe necrosis, architectural changes, and congestion. It was concluded that salbutamol showed better results however, spirulina also effectively reduced mild to moderate allergic symptoms in dose-dependent manner. Nutraceutical and functional foods are considered helpful in mitigating oxidative stress-mediated health problems. Spirulina has its unique nutritional profile including phycobiliproteins, phytochemicals, and antioxidant vitamins which make it useful against several ailments. Considering its antioxidant role, current study was focused on exploring therapeutic efficacy of spirulina against stress biomarkers in asthmatic model. Outcomes of present research also demonstrated beneficial effect of spirulina in modulating allergic symptoms. In this regard, ancient concept of "medicine food homology" can be implemented and spirulina can be incorporated in food for additional benefits. However, further research regarding safety aspects is needed for its use in clinical practice for humans.
Keywords: Ovalbumin; asthma; bronchoalveolar fluid; cigarette smoke; spirulina; stress biomarkers.
© 2022 The Authors. Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Standard technical specifications for methacholine chloride (Methacholine) bronchial challenge test (2023)].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2024 Feb 12;47(2):101-119. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112147-20231019-00247. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38309959 Chinese.
-
[Elevated expression of endothelin 2 in lung tissues of asthmatic rats after exposed to cigarette smoke and its mechanism].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2017 Aug;33(8):1030-1034. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28871941 Chinese.
-
The influence of Spirulina extract on pathogenicity, immune response, and vaccine efficacy against H9N2 avian influenza virus in specific pathogen free chickens.Poult Sci. 2024 Jan;103(1):103194. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2023.103194. Epub 2023 Oct 14. Poult Sci. 2024. PMID: 38041892 Free PMC article.
-
Mahuang decoction mitigates airway inflammation and regulates IL-21/STAT3 signaling pathway in rat asthma model.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Oct 5;224:373-380. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.06.011. Epub 2018 Jun 12. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29906536
-
Prophylactic role of olive fruit extract against cigarette smoke-induced oxidative stress in Sprague-Dawley rats.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2022 Sep;27(5):545-560. doi: 10.1007/s12192-022-01291-z. Epub 2022 Aug 11. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2022. PMID: 35951259 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Revealing the mechanism and efficacy of natural products on treating the asthma: Current insights from traditional medicine to modern drug discovery.Heliyon. 2024 May 28;10(11):e32008. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32008. eCollection 2024 Jun 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38882318 Free PMC article. Review.
-
C-Phycocyanin Prevents Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Lung Remodeling in an Ovalbumin-Induced Rat Asthma Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 27;25(13):7031. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137031. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000141 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdulmumin, A. N. (2013). Spirulina (Arthrospira): An important source of nutritional and medicinal compounds. Journal of the Marine Biological, 1, 1–7.
-
- Abdеlaziz, R. R. , Еlmahdy, M. , & Suddеk, G. M. (2018). Flavocoxid attenuates airway inflammation in ovalbumin‐induced mouse asthma model. Chemico‐Biological Interactions, 292, 15–23. - PubMed
-
- Alazemi, M. , Abdelhamy, A. , & Alsaeedi, A. (2018). The prevalence of smoking among sample of Kuwait Asthmatics and its impact on the response of the treatment. Journal of Pulmonary & Respiratory Medicine, 1, 4–10.
-
- Arashiro, L. T. , Boto‐Ordóñez, M. , Van Hulle, S. W. , Ferrer, I. , Garfí, M. , & Rousseau, D. P. (2020). Natural pigments from microalgae grown in industrial wastewater. Bioresource Technology, 303, 122894. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

