Septic cardiomyopathy: Diagnosis and management
- PMID: 36789232
- PMCID: PMC9923980
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jointm.2021.11.004
Septic cardiomyopathy: Diagnosis and management
Abstract
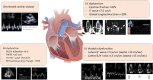
There is an extensive body of literature focused on sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction, but results are conflicting and no objective definition of septic cardiomyopathy (SCM) has been established. SCM may be defined as a sepsis-associated acute syndrome of non-ischemic cardiac dysfunction with systolic and/or diastolic left ventricular (LV) dysfunction and/or right ventricular dysfunction. Physicians should consider this diagnosis in patients with sepsis-associated organ dysfunction, and particularly in cases of septic shock that require vasopressors. Echocardiography is currently the gold standard for diagnosis of SCM. Left ventricular ejection fraction is the most common parameter used to describe LV function in the literature, but its dependence on loading conditions, particularly afterload, limits its use as a measure of intrinsic myocardial contractility. Therefore, repeated echocardiography evaluation is mandatory. Evaluation of global longitudinal strain (GLS) may be more sensitive and specific for SCM than LV ejection fraction (LVEF). Standard management includes etiological treatment, adapted fluid resuscitation, use of vasopressors, and monitoring. Use of inotropes remains uncertain, and heart rate control could be an option in some patients.
Keywords: Echocardiography; Myocardial dysfunction; Septic cardiomyopathy; Septic shock.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of Chinese Medical Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Ehrman R.R., Sullivan A.N., Favot M.J., Sherwin R.L., Reynolds C.A., Abidov A., et al. Pathophysiology, echocardiographic evaluation, biomarker findings, and prognostic implications of septic cardiomyopathy: a review of the literature. Crit Care. 2018;22(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s13054-018-2043-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

