Fake news, disinformation and misinformation in social media: a review
- PMID: 36789378
- PMCID: PMC9910783
- DOI: 10.1007/s13278-023-01028-5
Fake news, disinformation and misinformation in social media: a review
Abstract
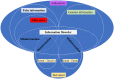
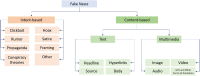
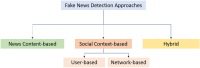
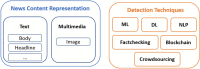
Online social networks (OSNs) are rapidly growing and have become a huge source of all kinds of global and local news for millions of users. However, OSNs are a double-edged sword. Although the great advantages they offer such as unlimited easy communication and instant news and information, they can also have many disadvantages and issues. One of their major challenging issues is the spread of fake news. Fake news identification is still a complex unresolved issue. Furthermore, fake news detection on OSNs presents unique characteristics and challenges that make finding a solution anything but trivial. On the other hand, artificial intelligence (AI) approaches are still incapable of overcoming this challenging problem. To make matters worse, AI techniques such as machine learning and deep learning are leveraged to deceive people by creating and disseminating fake content. Consequently, automatic fake news detection remains a huge challenge, primarily because the content is designed in a way to closely resemble the truth, and it is often hard to determine its veracity by AI alone without additional information from third parties. This work aims to provide a comprehensive and systematic review of fake news research as well as a fundamental review of existing approaches used to detect and prevent fake news from spreading via OSNs. We present the research problem and the existing challenges, discuss the state of the art in existing approaches for fake news detection, and point out the future research directions in tackling the challenges.
Keywords: Disinformation; Fake news; Information disorder; Misinformation; Online deception; Online social networks.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Austria, part of Springer Nature 2023, Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestOn behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures


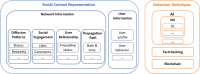
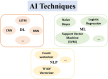
References
-
- Abdullah-All-Tanvir, Mahir EM, Akhter S, Huq MR (2019) Detecting fake news using machine learning and deep learning algorithms. In: 7th international conference on smart computing and communications (ICSCC), IEEE, pp 1–5 10.1109/ICSCC.2019.8843612
-
- Abdullah-All-Tanvir, Mahir EM, Huda SMA, Barua S (2020) A hybrid approach for identifying authentic news using deep learning methods on popular Twitter threads. In: International conference on artificial intelligence and signal processing (AISP), IEEE, pp 1–6 10.1109/AISP48273.2020.9073583
-
- Abu Arqoub O, Abdulateef Elega A, Efe Özad B, Dwikat H, Adedamola Oloyede F. Mapping the scholarship of fake news research: a systematic review. J Pract. 2022;16(1):56–86. doi: 10.1080/17512786.2020.1805791. - DOI
-
- Ahmed S, Hinkelmann K, Corradini F. Development of fake news model using machine learning through natural language processing. Int J Comput Inf Eng. 2020;14(12):454–460.
-
- Aïmeur E, Brassard G, Rioux J. Data privacy: an end-user perspective. Int J Comput Netw Commun Secur. 2013;1(6):237–250.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
