Autophagy and its role in osteosarcoma
- PMID: 36789748
- PMCID: PMC10028045
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.5407
Autophagy and its role in osteosarcoma
Abstract
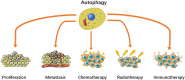
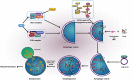
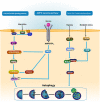
Osteosarcoma (OS) is the most common bone malignancy and preferably occurs in children and adolescents. Despite significant advances in surgery and chemotherapy for OS over the past few years, overall survival rates of OS have reached a bottleneck. Thus, extensive researches aimed at developing new therapeutic targets for OS are urgently needed. Autophagy, a conserved process which allows cells to recycle altered or unused organelles and cellular components, has been proven to play a critical role in multiple biological processes in OS. In this article, we summarized the association between autophagy and proliferation, metastasis, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and immunotherapy of OS, revealing that autophagy-related genes and pathways could serve as potential targets for OS therapy.
Keywords: autophagy; chemotherapy; immunotherapy; osteosarcoma; progression; radiotherapy.
© 2023 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors acknowledge that there is no conflict of interest in this review.
Figures
References
-
- Longhi A, Errani C, De Paolis M, Mercuri M, Bacci G. Primary bone osteosarcoma in the pediatric age: state of the art. Cancer Treat Rev. 2006;32(6):423‐436. - PubMed
-
- Esiashvili N, Goodman M, Marcus RB Jr. Changes in incidence and survival of Ewing sarcoma patients over the past 3 decades: surveillance epidemiology and end results data. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2008;30(6):425‐430. - PubMed
-
- Cho WH, Song WS, Jeon DG, et al. Differential presentations, clinical courses, and survivals of osteosarcomas of the proximal humerus over other extremity locations. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17(3):702‐708. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous