Traditional Chinese medicine Euodiae Fructus: botany, traditional use, phytochemistry, pharmacology, toxicity and quality control
- PMID: 36790599
- PMCID: PMC9931992
- DOI: 10.1007/s13659-023-00369-0
Traditional Chinese medicine Euodiae Fructus: botany, traditional use, phytochemistry, pharmacology, toxicity and quality control
Abstract
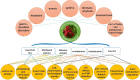
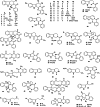
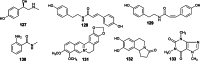
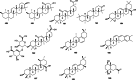
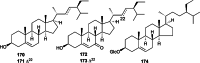
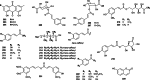
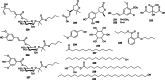
Euodiae Fructus, referred to as "Wuzhuyu" in Chinese, has been used as local and traditional herbal medicines in many regions, especially in China, Japan and Korea, for the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders, headache, emesis, aphtha, dermatophytosis, dysentery, etc. Substantial investigations into their chemical and pharmacological properties have been performed. Recently, interest in this plant has been focused on the different structural types of alkaloids like evodiamine, rutaecarpine, dehydroevodiamine and 1-methyl-2-undecyl-4(1H)-quinolone, which exhibit a wide range of pharmacological activities in preclinical models, such as anticancer, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, anti-cardiovascular disease, etc. This review summarizes the up-to-date and comprehensive information concerning the botany, traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology of Euodiae Fructus together with the toxicology and quality control, and discusses the possible direction and scope for future research on this plant.
Keywords: Euodiae Fructus; Pharmacology; Phytochemistry; Toxicology; Traditional uses.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
Grants and funding
- 82004215/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82173704/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 31870327/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82003624/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82004003/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2019YFC1711006/the Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2017YFC1702002/the Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2018ZX09731016-005/the National Major Project of China
- 16DZ2280200/Shanghai Engineering Research Center for the Preparation of Bioactive Natural Products
- 20204Y0326/Shanghai Municipal Health Commission Project
- 20YF1459000/Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality
- 20YF1458700/Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

