Metagenomic analysis of Ancient Egyptian canopic jars
- PMID: 36790695
- PMCID: PMC9804471
- DOI: 10.1002/ajpa.24600
Metagenomic analysis of Ancient Egyptian canopic jars
Abstract
Ancient Egyptian remains have been of interest for anthropological research for decades. Despite many investigations, the ritual vessels for the internal organs removed during body preparation-liver, lungs, stomach, and intestines, of Egyptian mummies are rarely used for palaeopathological or medical investigations. These artifacts, commonly referred to as canopic jars, are the perfect combination of cultural and biological material and present an untapped resource for both Egyptological and medical fields. Nevertheless, technical challenges associated with this archeological material have prevented the application of current ancient DNA techniques for both the characterization of human and pathogenic DNA. We present shotgun-sequenced metagenomic profiles and ancient DNA degradation patterns from multiple canopic jars sampled from several European museum collections and enumerate current limitations and possible solutions for the future analysis of similar material. This is the first-ever recorded evidence of ancient human DNA found in Ancient Egyptian canopic jars and the first associated metagenomic description of bacterial taxa in these funerary artifacts.
Objectives: In this study, our objectives were to characterize the metagenomic profile of the Ancient Egyptian funerary vessels known as canopic jars to retrieve endogenous ancient human DNA, reconstruct ancient microbial communities, and identify possible pathogens that could shed light on disease states of individuals from the past.
Methods: We applied ancient DNA techniques on 140 canopic jars to extract DNA and generate whole-genome sequencing libraries for the analysis of both human and bacterial DNA. The samples were obtained from museum collections in Berlin (DE), Burgdorf (DE), Leiden (NE), Manchester (UK), Munich (DE), St. Gallen (CH), Turin (IT), and Zagreb (HR).
Results: Here we describe the first isolated DNA from the Egyptian artifacts that hold human viscera. No previous work was ever conducted on such material, which led to the first characterization of human DNA from Ancient Egyptian canopic jars and the profiling of the complex bacterial composition of this highly degraded, challenging, organic material. However, the DNA recovered was not of enough quality to confidently characterize bacterial taxa associated with infectious diseases, nor exclusive bacterial members of the human microbiome.
Discussion: In summary, we present the first genomic survey of the visceral content of Ancient Egyptian funerary artifacts and demonstrate the limitations of current molecular methods to analyze canopic jars, such as the incomplete history of the objects or the presence of uncharacterized compounds that can hamper the recovery of DNA. Our work highlights the main challenges and caveats when working with such complicated archeological material - and offers sampling recommendations for similarly complex future studies, such as incrementing the amount of starting material and sampling from the less exposed parts of the jar content. This is the first-ever recorded evidence of ancient human DNA found in Ancient Egyptian canopic jars, and our results open new avenues in the study of neglected archeological artifacts.
Keywords: Ancient Egypt; ancient DNA; canopic jars; metagenomics.
© 2022 The Authors. American Journal of Biological Anthropology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Figures
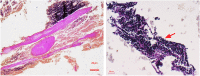
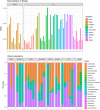
Similar articles
-
Egyptian Canopic Jars at the Crossroad of Medicine and Archaeology: Overview of 100 Years of Research and Future Scientific Expectations.Pathobiology. 2018;85(5-6):267-275. doi: 10.1159/000490797. Epub 2018 Aug 21. Pathobiology. 2018. PMID: 30130765 Review.
-
Reshaping Egyptian funerary ritual in colonized Nubia? Organic characterization of unguents from mortuary contexts of the New Kingdom (c. 1550-1070 BCE).Archaeol Anthropol Sci. 2023;15(6):73. doi: 10.1007/s12520-023-01769-6. Epub 2023 May 8. Archaeol Anthropol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37181044 Free PMC article.
-
Radiological findings in ancient Egyptian canopic jars: comparing three standard clinical imaging modalities (x-rays, CT and MRI).Eur Radiol Exp. 2018 Jun 20;2:12. doi: 10.1186/s41747-018-0048-3. eCollection 2018 Dec. Eur Radiol Exp. 2018. PMID: 29951641 Free PMC article.
-
Untargeted metabolomics-like screening approach for chemical characterization and differentiation of canopic jar and mummy samples from Ancient Egypt using GC-high resolution MS.Analyst. 2018 Sep 21;143(18):4503-4512. doi: 10.1039/c8an01288a. Epub 2018 Aug 31. Analyst. 2018. PMID: 30168542
-
Insights from ancient DNA analysis of Egyptian human mummies: clues to disease and kinship.Hum Mol Genet. 2021 Apr 26;30(R1):R24-R28. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddaa223. Hum Mol Genet. 2021. PMID: 33059357 Review.
References
-
- Brockbals, L. , Habicht, M. , Hajdas, I. , Galassi, F. M. , Rühli, F. J. , & Kraemer, T. (2018). Untargeted metabolomics‐like screening approach for chemical characterization and differentiation of canopic jar and mummy samples from ancient Egypt using GC‐high resolution MS. The Analyst, 143(18), 4503–4512. - PubMed
-
- Dabney, J. , Knapp, M. , Glocke, I. , Gansauge, M.‐T. , Weihmann, A. , Nickel, B. , Valdiosera, C. , García, N. , Pääbo, S. , Arsuaga, J.‐L. , & Meyer, M. (2013). Complete mitochondrial genome sequence of a middle Pleistocene cave bear reconstructed from ultrashort DNA fragments. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 110(39), 15758–15763. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dicks, L. , & Endo, A. (2014). The family Lactobacillaceae: Genera other than Lactobacillus . In Rosenberg E., DeLong E. F., Lory S., Stackebrandt E., & Thompson F. (Eds.), The prokaryotes: Firmicutes and tenericutes (pp. 203–212). Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
