Metformin and Dapagliflozin Attenuate Doxorubicin-Induced Acute Cardiotoxicity in Wistar Rats: An Electrocardiographic, Biochemical, and Histopathological Approach
- PMID: 36790727
- PMCID: PMC9950216
- DOI: 10.1007/s12012-023-09784-8
Metformin and Dapagliflozin Attenuate Doxorubicin-Induced Acute Cardiotoxicity in Wistar Rats: An Electrocardiographic, Biochemical, and Histopathological Approach
Abstract
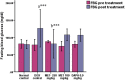
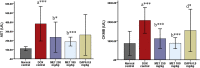
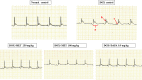
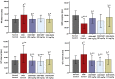
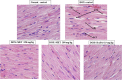
Doxorubicin is a widely used anticancer drug whose efficacy is limited due to its cardiotoxicity. There is no ideal cardioprotection available against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. This study aimed to investigate the anticipated cardioprotective potential of metformin and dapagliflozin against doxorubicin-induced acute cardiotoxicity in Wistar rats. At the beginning of the experiment, cardiac screening of experimental animals was done by recording an electrocardiogram (ECG) before allocating them into the groups. Thereafter, a total of thirty healthy adult Wistar rats (150-200 g) were randomly divided into five groups (n = 6) and treated for eight days as follows: group I (normal control), group II (doxorubicin control), group III (metformin 250 mg/kg/day), group IV (metformin 180 mg/kg/day), and group V (dapagliflozin 0.9 mg/kg/day). On the 7th day of the treatment phase, doxorubicin 20 mg/kg was administered intraperitoneal to groups II, III, IV, and V. On the 9th day (immediately after 48 h of doxorubicin administration), blood was collected from anesthetized animals for glucose, lipid profile, CK-MB & AST estimation, and ECG was recorded. Later, animals were sacrificed, and the heart was dissected for histopathological examination. We found that compared to normal control rats, CK-MB, AST, and glucose were significantly increased in doxorubicin control rats. There was a significant reversal of doxorubicin-induced hyperglycemia in the rats treated with metformin 250 mg/kg compared to doxorubicin control rats. Both metformin (180 mg/kg and 250 mg/kg) and dapagliflozin (0.9 mg/kg) significantly altered doxorubicin-induced ECG changes and reduced the levels of cardiac injury biomarkers CK-MB and AST compared to doxorubicin control rats. Metformin and dapagliflozin protected the cellular architecture of the myocardium from doxorubicin-induced myocardial injury. Current study revealed that both metformin and dapagliflozin at the FDA-recommended antidiabetic doses mitigated doxorubicin-induced acute cardiotoxicity in Wistar rats. The obtained data have opened the perspective to perform chronic studies and then to clinical studies to precisely consider metformin and dapagliflozin as potential chemoprotection in the combination of chemotherapy with doxorubicin to limit its cardiotoxicity, especially in patients with comorbid conditions like type II diabetes mellitus.
Keywords: Antidiabetic drugs; Cardio-oncology; Cardiotoxicity; Chemoprotectant; Chemotherapy; Electrocardiograph.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article. All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chia Seed Oil Ameliorates Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Female Wistar Rats: An Electrocardiographic, Biochemical and Histopathological Approach.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2021 Jul;21(7):533-542. doi: 10.1007/s12012-021-09644-3. Epub 2021 Mar 19. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33740233 Free PMC article.
-
Combined effects of metformin and coenzyme Q10 on doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in male wistar rats.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):20725. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-07576-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40596564 Free PMC article.
-
Methyl Gallate Attenuates Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Rats by Suppressing Oxidative Stress.Scientifica (Cairo). 2021 Jan 13;2021:6694340. doi: 10.1155/2021/6694340. eCollection 2021. Scientifica (Cairo). 2021. PMID: 33510932 Free PMC article.
-
Cardioprotective effects of melatonin and metformin against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats are through preserving mitochondrial function and dynamics.Biochem Pharmacol. 2021 Oct;192:114743. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114743. Epub 2021 Aug 26. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34453902
-
Exploiting the cardioprotective potential of metformin against cardiotoxic agents.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 16. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04378-3. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40524049 Review.
Cited by
-
The Cardioprotective and Anticancer Effects of SGLT2 Inhibitors: JACC: CardioOncology State-of-the-Art Review.JACC CardioOncol. 2024 Mar 12;6(2):159-182. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccao.2024.01.007. eCollection 2024 Apr. JACC CardioOncol. 2024. PMID: 38774006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardioprotective Effects of Dapagliflozin and Trimetazidine on Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Streptozotocin-Induced Type 1 Diabetic Rats via Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress.J Clin Med. 2025 Feb 16;14(4):1315. doi: 10.3390/jcm14041315. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40004844 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms involved in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: A bibliometrics analysis by VOSviewer.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Apr;397(4):1971-1984. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02773-2. Epub 2023 Oct 9. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37812241 Review.
-
Combination Therapy with Vitamin D and Metformin: A Potential Approach to Mitigate Testicular Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Reprod Sci. 2024 Dec;31(12):3795-3807. doi: 10.1007/s43032-024-01708-3. Epub 2024 Sep 25. Reprod Sci. 2024. PMID: 39317887
-
Cardioprotective potential of protocatechuic acid against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats.Res Pharm Sci. 2025 Feb 20;20(1):55-64. doi: 10.4103/RPS.RPS_220_23. eCollection 2025 Feb. Res Pharm Sci. 2025. PMID: 40190819 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

