Ultrasonic Vitrectomy Performance Assessment Using Micro-Extensional Rheology
- PMID: 36790819
- PMCID: PMC9940767
- DOI: 10.1167/tvst.12.2.24
Ultrasonic Vitrectomy Performance Assessment Using Micro-Extensional Rheology
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to assess the performance of ultrasonic (US) vitrectomy devices by quantifying and comparing its impact on extracted vitreous properties to conventional pneumatic blade (PB) cutters using micro-extensional rheology. US vitrectomy is a new technology that offers an alternative to PB cutters used in vitreo-retinal surgeries.
Methods: Thirty-six porcine vitreous samples were extracted using US and PB cutters. Each sample was kept at 4°C and tested within 24 hours postmortem and 4 hours post-vitrectomy. A recently developed micro-extensional rheology technique is used to infer the relative protein fragment size of extracted vitreous by quantifying the extensional relaxation time.
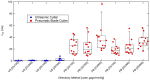
Results: US-extracted vitreous exhibited extensional relaxation times orders of magnitude lower than PB-extracted vitreous (0.37 ms and 27.25 ms, respectively). Relaxation time is directly correlated to the fragment size of the collagen fibers in the vitreous. The formation of beads-on-a-string droplets within the PB samples indicates the presence of larger collagen fragments. These droplets were not seen on US samples.
Conclusions: This new micro-extensional rheology technique can identify significant differences in physical properties of extracted vitreous. Long relaxation times and beads-on-a-string droplets within the PB vitreous samples indicate larger protein fragments compared to the US samples.
Translational relevance: Higher fragmentation of vitreous and lower extensional relaxation times may improve retina safety due to a reduction in vitreo-retinal traction resulting from the continuous shear action and aspiration applied by ultrasonic vitrectomy technology.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures




Similar articles
-
Novel probabilistic model of core vitreous traction using microsurgical vitrectomy tools.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2021 Feb;259(2):405-412. doi: 10.1007/s00417-020-04836-z. Epub 2020 Aug 18. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 32809071
-
Experimental assessment of the performance of vitreous cutters with fluids with different rheological properties.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2021 May;259(5):1113-1121. doi: 10.1007/s00417-020-05061-4. Epub 2021 Jan 4. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 33394160
-
Vitreoretinal traction created by conventional cutters during vitrectomy.Ophthalmology. 2010 Jul;117(7):1387-92.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2009.11.004. Epub 2010 Feb 21. Ophthalmology. 2010. PMID: 20176400
-
[Pars plana vitrectomy-from suction cutting systems to ultrasound technology : Vitesse-a new form of vitrectomy based on ultrasound technology].Ophthalmologe. 2021 Jul;118(7):741-746. doi: 10.1007/s00347-021-01377-6. Epub 2021 Apr 20. Ophthalmologe. 2021. PMID: 33877403 Free PMC article. Review. German.
-
Novel vitreous modulators for pharmacologic vitreolysis in the treatment of diabetic retinopathy.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2011 Mar 1;12(3):410-22. doi: 10.2174/138920111794480516. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 20939794 Review.
Cited by
-
An Inverse Method to Determine Mechanical Parameters of Porcine Vitreous Bodies Based on the Indentation Test.Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 May 26;10(6):646. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10060646. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37370577 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bishop PN. Structural macromolecules and supramolecular organisation of the vitreous gel. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2000; 19(3): 323–344. - PubMed
-
- Sebag J, Balazs EA.. Morphology and ultrastructure of human vitreous fibers. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1989; 30(8): 1867–1871. - PubMed
-
- Foulds WS. Is your vitreous really necessary? Eye. 1987; 1(6): 641–664. - PubMed
-
- Rossi T, Querzoli G, Angelini G, et al. .. Fluid dynamics of vitrectomy probes. Retina. 2014; 34(3): 558–567. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

