Evaluation of BNT162b2 Covid-19 Vaccine in Children Younger than 5 Years of Age
- PMID: 36791162
- PMCID: PMC9947923
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2211031
Evaluation of BNT162b2 Covid-19 Vaccine in Children Younger than 5 Years of Age
Abstract
Background: Safe and effective vaccines against coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) are urgently needed in young children.
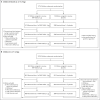
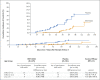
Methods: We conducted a phase 1 dose-finding study and are conducting an ongoing phase 2-3 safety, immunogenicity, and efficacy trial of the BNT162b2 vaccine in healthy children 6 months to 11 years of age. We present results for children 6 months to less than 2 years of age and those 2 to 4 years of age through the data-cutoff dates (April 29, 2022, for safety and immunogenicity and June 17, 2022, for efficacy). In the phase 2-3 trial, participants were randomly assigned (in a 2:1 ratio) to receive two 3-μg doses of BNT162b2 or placebo. On the basis of preliminary immunogenicity results, a third 3-μg dose (≥8 weeks after dose 2) was administered starting in January 2022, which coincided with the emergence of the B.1.1.529 (omicron) variant. Immune responses at 1 month after doses 2 and 3 in children 6 months to less than 2 years of age and those 2 to 4 years of age were immunologically bridged to responses after dose 2 in persons 16 to 25 years of age who received 30 μg of BNT162b2 in the pivotal trial.
Results: During the phase 1 dose-finding study, two doses of BNT162b2 were administered 21 days apart to 16 children 6 months to less than 2 years of age (3-μg dose) and 48 children 2 to 4 years of age (3-μg or 10-μg dose). The 3-μg dose level was selected for the phase 2-3 trial; 1178 children 6 months to less than 2 years of age and 1835 children 2 to 4 years of age received BNT162b2, and 598 and 915, respectively, received placebo. Immunobridging success criteria for the geometric mean ratio and seroresponse at 1 month after dose 3 were met in both age groups. BNT162b2 reactogenicity events were mostly mild to moderate, with no grade 4 events. Low, similar incidences of fever were reported after receipt of BNT162b2 (7% among children 6 months to <2 years of age and 5% among those 2 to 4 years of age) and placebo (6 to 7% among children 6 months to <2 years of age and 4 to 5% among those 2 to 4 years of age). The observed overall vaccine efficacy against symptomatic Covid-19 in children 6 months to 4 years of age was 73.2% (95% confidence interval, 43.8 to 87.6) from 7 days after dose 3 (on the basis of 34 cases).
Conclusions: A three-dose primary series of 3-μg BNT162b2 was safe, immunogenic, and efficacious in children 6 months to 4 years of age. (Funded by BioNTech and Pfizer; ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT04816643.).
Copyright © 2023 Massachusetts Medical Society.
Figures

Comment in
-
Impact of COVID-19 on mortality under 5 years old.Pediatr Res. 2023 Nov;94(5):1592. doi: 10.1038/s41390-023-02612-3. Epub 2023 Apr 17. Pediatr Res. 2023. PMID: 37069225 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Laboratory-confirmed COVID-19-associated hospitalizations (https://gis.cdc.gov/grasp/COVIDNet/COVID19_5.html).
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID data tracker: health department-reported cases of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) in the United States (https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#mis-national-surveillance).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
