Thrombospondin-1, CD47, and SIRPα display cell-specific molecular signatures in human islets and pancreata
- PMID: 36791324
- PMCID: PMC11967708
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00221.2022
Thrombospondin-1, CD47, and SIRPα display cell-specific molecular signatures in human islets and pancreata
Abstract
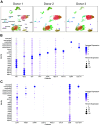
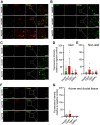
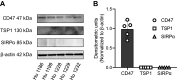
Thrombospondin-1 (TSP1) is a secreted protein minimally expressed in health but increased in disease and age. TSP1 binds to the cell membrane receptor CD47, which itself engages signal regulatory protein α (SIRPα), and the latter creates a checkpoint for immune activation. Individuals with cancer administered checkpoint-blocking molecules developed insulin-dependent diabetes. Relevant to this, CD47 blocking antibodies and SIRPα fusion proteins are in clinical trials. We characterized the molecular signature of TSP1, CD47, and SIRPα in human islets and pancreata. Fresh islets and pancreatic tissue from nondiabetic individuals were obtained. The expression of THBS1, CD47, and SIRPA was determined using single-cell mRNA sequencing, immunofluorescence microscopy, Western blot, and flow cytometry. Islets were exposed to diabetes-affiliated inflammatory cytokines and changes in protein expression were determined. CD47 mRNA was expressed in all islet cell types. THBS1 mRNA was restricted primarily to endothelial and mesenchymal cells, whereas SIRPA mRNA was found mostly in macrophages. Immunofluorescence staining showed CD47 protein expressed by β cells and present in the exocrine pancreas. TSP1 and SIRPα proteins were not seen in islets or the exocrine pancreas. Western blot and flow cytometry confirmed immunofluorescent expression patterns. Importantly, human islets produced substantial quantities of secreted TSP1. Human pancreatic exocrine and endocrine tissue expressed CD47, whereas fresh islets displayed cell surface CD47 and secreted TSP1 at baseline and in inflammation. These findings suggest unexpected effects on islets from agents that intersect TSP1-CD47-SIRPα.NEW & NOTEWORTHY CD47 is a cell surface receptor with two primary ligands, soluble thrombospondin-1 (TSP1) and cell surface signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPα). Both interactions provide checkpoints for immune cell activity. We determined that fresh human islets display CD47 and secrete TSP1. However, human islet endocrine cells lack SIRPα. These gene signatures are likely important given the increasing use of CD47 and SIRPα blocking molecules in individuals with cancer.
Keywords: CD47; SIRPα; islets; thrombospondin-1; type 1 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures


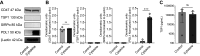
References
-
- Kaur S, Soto-Pantoja DR, Stein EV, Liu C, Elkahloun AG, Pendrak ML, Nicolae A, Singh SP, Nie Z, Levens D, Isenberg JS, Roberts DD. Thrombospondin-1 signaling through CD47 inhibits self-renewal by regulating c-Myc and other stem cell transcription factors. Sci Rep 3: 1673, 2013. doi: 10.1038/srep01673. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Isenberg JS, Hyodo F, Matsumoto K-I, Romeo MJ, Abu-Asab M, Tsokos M, Kuppusamy P, Wink DA, Krishna MC, Roberts DD. Thrombospondin-1 limits ischemic tissue survival by inhibiting nitric oxide-mediated vascular smooth muscle relaxation. Blood 109: 1945–1952, 2007. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-08-041368. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Csanyi G, Yao M, Rodriguez AI, Al Ghouleh I, Sharifi-Sanjani M, Frazziano G, Huang X, Kelley EE, Isenberg JS, Pagano PJ. Thrombospondin-1 regulates blood flow via CD47 receptor-mediated activation of NADPH oxidase 1. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 32: 2966–2973, 2012. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.300031. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

