Chemoproteomic discovery of a human RNA ligase
- PMID: 36792600
- PMCID: PMC9931718
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-36451-x
Chemoproteomic discovery of a human RNA ligase
Abstract
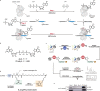
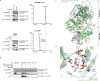
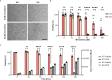
RNA ligases are present across all forms of life. While enzymatic RNA ligation between 5'-PO4 and 3'-OH termini is prevalent in viruses, fungi, and plants, such RNA ligases are yet to be identified in vertebrates. Here, using a nucleotide-based chemical probe targeting human AMPylated proteome, we have enriched and identified the hitherto uncharacterised human protein chromosome 12 open reading frame 29 (C12orf29) as a human enzyme promoting RNA ligation between 5'-PO4 and 3'-OH termini. C12orf29 catalyses ATP-dependent RNA ligation via a three-step mechanism, involving tandem auto- and RNA AMPylation. Knock-out of C12ORF29 gene impedes the cellular resilience to oxidative stress featuring concurrent RNA degradation, which suggests a role of C12orf29 in maintaining RNA integrity. These data provide the groundwork for establishing a human RNA repair pathway.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

