Long noncoding RNA ENST00000436340 promotes podocyte injury in diabetic kidney disease by facilitating the association of PTBP1 with RAB3B
- PMID: 36792603
- PMCID: PMC9932062
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-023-05658-7
Long noncoding RNA ENST00000436340 promotes podocyte injury in diabetic kidney disease by facilitating the association of PTBP1 with RAB3B
Abstract
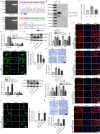
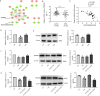
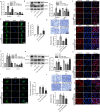
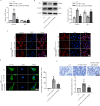
Dysfunction of podocytes has been regarded as an important early pathologic characteristic of diabetic kidney disease (DKD), but the regulatory role of long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) in this process remains largely unknown. Here, we performed RNA sequencing in kidney tissues isolated from DKD patients and nondiabetic renal cancer patients undergoing surgical resection and discovered that the novel lncRNA ENST00000436340 was upregulated in DKD patients and high glucose-induced podocytes, and we showed a significant correlation between ENST00000436340 and kidney injury. Gain- and loss-of-function experiments showed that silencing ENST00000436340 alleviated high glucose-induced podocyte injury and cytoskeleton rearrangement. Mechanistically, we showed that fat mass and obesity- associate gene (FTO)-mediated m6A induced the upregulation of ENST00000436340. ENST00000436340 interacted with polypyrimidine tract binding protein 1 (PTBP1) and augmented PTBP1 binding to RAB3B mRNA, promoted RAB3B mRNA degradation, and thereby caused cytoskeleton rearrangement and inhibition of GLUT4 translocation to the plasma membrane, leading to podocyte injury and DKD progression. Together, our results suggested that upregulation of ENST00000436340 could promote podocyte injury through PTBP1-dependent RAB3B regulation, thus suggesting a novel form of lncRNA-mediated epigenetic regulation of podocytes that contributes to the pathogenesis of DKD.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
FTO-mediated m6A modification of serum amyloid A2 mRNA promotes podocyte injury and inflammation by activating the NF-κB signaling pathway.FASEB J. 2024 Jan 31;38(2):e23409. doi: 10.1096/fj.202301419RR. FASEB J. 2024. PMID: 38193628
-
Long Noncoding RNA ENSG00000254693 Promotes Diabetic Kidney Disease via Interacting with HuR.J Diabetes Res. 2022 Apr 19;2022:8679548. doi: 10.1155/2022/8679548. eCollection 2022. J Diabetes Res. 2022. PMID: 35493610 Free PMC article.
-
Increased long noncoding RNA maternally expressed gene 3 contributes to podocyte injury induced by high glucose through regulation of mitochondrial fission.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Sep 29;11(9):814. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03022-7. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32994406 Free PMC article.
-
PTBP1 as a potential regulator of disease.Mol Cell Biochem. 2024 Nov;479(11):2875-2894. doi: 10.1007/s11010-023-04905-x. Epub 2023 Dec 22. Mol Cell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38129625 Review.
-
Long noncoding RNA: an emerging player in diabetes and diabetic kidney disease.Clin Sci (Lond). 2019 Jun 20;133(12):1321-1339. doi: 10.1042/CS20190372. Print 2019 Jun 28. Clin Sci (Lond). 2019. PMID: 31221822 Review.
Cited by
-
Kidney Injury: Focus on Molecular Signaling Pathways.Curr Med Chem. 2024;31(28):4510-4533. doi: 10.2174/0109298673271547231108060805. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38314680 Review.
-
Epigenetic modification in diabetic kidney disease.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jun 30;14:1133970. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1133970. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37455912 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LncRNA evf-2 Exacerbates Podocyte Injury in Diabetic Nephropathy by Inducing Cell Cycle Re-entry and Inflammation Through Distinct Mechanisms Triggered by hnRNPU.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Dec;11(47):e2406532. doi: 10.1002/advs.202406532. Epub 2024 Oct 29. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 39470303 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA AA465934 Improves Podocyte Injury by Promoting Tristetraprolin-Mediated HMGB1 DownRegulation in Diabetic Nephropathy.Mol Cell Biol. 2024;44(3):87-102. doi: 10.1080/10985549.2024.2325527. Epub 2024 Mar 23. Mol Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38520226 Free PMC article.
-
m6A Ribonucleic Acid Methylation in Fibrotic Diseases of Visceral Organs.Small Sci. 2024 Nov 21;5(2):2400308. doi: 10.1002/smsc.202400308. eCollection 2025 Feb. Small Sci. 2024. PMID: 40213062 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

