CRISPR/Cas9-mediated targeted knock-in of large constructs using nocodazole and RNase HII
- PMID: 36792645
- PMCID: PMC9931768
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-29789-1
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated targeted knock-in of large constructs using nocodazole and RNase HII
Abstract
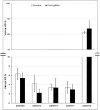
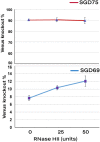
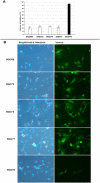
On-target integration of large cassettes via homology-directed repair (HDR) has several applications. However, the HDR-mediated targeted knock-in suffered from low efficiency. In this study, we made several large plasmids (12.1-13.4 kb) which included the CRISPR/Cas9 system along with a puromycin transgene as part of the large DNA donor (5.3-7.1 kb insertion cassettes) and used them to evaluate their targeted integration efficiency into a transgenic murine embryonic fibroblast (MEF) cell line carrying a single copy of a Venus transgene. We established a detection assay by which HDR events could be discriminated from the error-prone non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) events. Improving the plasmid quality could considerably leverage the cell toxicity impediment of large plasmids. The use of the TILD (targeted integration with linearized dsDNA) cassettes did not improve the HDR rate compared to the circular plasmids. However, the direct inclusion of nocodazole into the electroporation solution significantly improved the HDR rate. Also, simultaneous delivery of RNase HII and the donor plasmids into the electroporated cells considerably improved the HDR events. In conclusion, the results of this study showed that using cell synchronization reagents in the electroporation medium can efficiently induce HDR rate in the mammalian genome.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
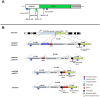
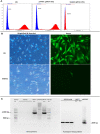
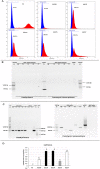
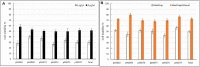
Similar articles
-
Combi-CRISPR: combination of NHEJ and HDR provides efficient and precise plasmid-based knock-ins in mice and rats.Hum Genet. 2021 Feb;140(2):277-287. doi: 10.1007/s00439-020-02198-4. Epub 2020 Jul 2. Hum Genet. 2021. PMID: 32617796 Free PMC article.
-
Highly efficient CRISPR/HDR-mediated knock-in for mouse embryonic stem cells and zygotes.Biotechniques. 2015 Oct 1;59(4):201-2, 204, 206-8. doi: 10.2144/000114339. eCollection 2015 Oct. Biotechniques. 2015. PMID: 26458548
-
Efficient biallelic knock-in in mouse embryonic stem cells by in vivo-linearization of donor and transient inhibition of DNA polymerase θ/DNA-PK.Sci Rep. 2021 Sep 13;11(1):18132. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-97579-8. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34518609 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies for generation of mice via CRISPR/HDR-mediated knock-in.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Apr;50(4):3189-3204. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08278-8. Epub 2023 Jan 26. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 36701041 Review.
-
Opportunities and challenges with CRISPR-Cas mediated homologous recombination based precise editing in plants and animals.Plant Mol Biol. 2023 Jan;111(1-2):1-20. doi: 10.1007/s11103-022-01321-5. Epub 2022 Oct 31. Plant Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36315306 Review.
Cited by
-
Time and Cost-Effective Genome Editing Protocol for Simultaneous Caspase 8 Associated Protein 2 Gene Knock in/out in Chinese Hamster Ovary Cells Using CRISPR-Cas9 System.Iran J Biotechnol. 2024 Jan 1;22(1):e3714. doi: 10.30498/ijb.2024.398567.3714. eCollection 2024 Jan. Iran J Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38827341 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated base editors and their prospects for mitochondrial genome engineering.Gene Ther. 2024 May;31(5-6):209-223. doi: 10.1038/s41434-023-00434-w. Epub 2024 Jan 4. Gene Ther. 2024. PMID: 38177342 Review.
-
Robust and cost-effective CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing of primary tumor B cells in Eµ-TCL1 model of chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Hemasphere. 2024 Aug 15;8(8):e134. doi: 10.1002/hem3.134. eCollection 2024 Aug. Hemasphere. 2024. PMID: 39157689 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Editorial: Genetics of reproduction for livestock species.Front Genet. 2023 May 22;14:1210904. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1210904. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37284063 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Increasing Knockin Efficiency in Mouse Zygotes by Transient Hypothermia.CRISPR J. 2024 Apr;7(2):111-119. doi: 10.1089/crispr.2023.0077. CRISPR J. 2024. PMID: 38635329 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Houdebine L-M. Transgenic Animals. CRC Press; 1997.
-
- Marks, D. et al. The method of choice to knock-in large inserts via CRISPR. bioRxiv (2021).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

