Psychological status of infertile men during the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic in China: a cross-sectional investigation
- PMID: 36792987
- PMCID: PMC9931448
- DOI: 10.1186/s12610-022-00177-5
Psychological status of infertile men during the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic in China: a cross-sectional investigation
Abstract
Background: The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak has had a widespread and profound impact on people's mental health. The factors associated with mental symptoms among men diagnosed with infertility, a disease closely related to psychological conditions, remain unclear. The aim of this study is to investigate the risk factors associated with mental symptoms among infertile Chinese men during the pandemic.
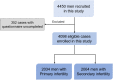
Results: A total of 4,098 eligible participants were recruited in this cross-sectional, nationwide study, including 2,034 (49.6%) with primary infertility and 2,064 (50.4%) with secondary infertility. The prevalence of mental health conditions was 36.3%, 39.6%, and 6.7% for anxiety, depression, and post-pandemic stress, respectively. Sexual dysfunction is associated with a higher risk with adjusted odds ratios (ORs) of 1.40 for anxiety, 1.38 for depression, and 2.32 for stress. Men receiving infertility drug therapy displayed a higher risk for anxiety (adjusted OR, 1.31) and depression (adjusted OR, 1.28) symptoms, while those receiving intrauterine insemination had a lower risk of anxiety (adjusted OR, 0.56) and depression (adjusted OR, 0.55) symptoms.
Conclusion: The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant psychological impact on infertile men. Several psychologically vulnerable populations were identified, including individuals with sexual dysfunction, respondents receiving infertility drug therapy, and those experiencing control measures for COVID-19. The findings provide a comprehensive profile of the mental health status of infertile Chinese men during the COVID-19 outbreak and provide potential psychological intervention strategies.
RéSUMé: CONTEXTE: L’épidémie de maladie à coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) a eu un impact étendu et profond sur la santé mentale des gens. Les facteurs associés aux symptômes mentaux chez les hommes diagnostiqués comme infertiles, une maladie étroitement liée aux conditions psychologiques, restent flous. L’objectif de cette étude est d’étudier les facteurs de risque associés aux symptômes mentaux chez les hommes chinois infertiles pendant la pandémie. RéSULTATS: Au total, 4 098 participants admissibles ont été recrutés dans cette étude transversale à l’échelle nationale, dont 2 034 (49,6%) présentaient une infertilité primaire et 2 064 (50,4%) une infertilité secondaire. La prévalence des problèmes de santé mentale était respectivement de 36,3 %, 39,6 % et 6,7 % pour l’anxiété, la dépression, et le stress postpandémique. La dysfonction sexuelle est associée à un risque plus élevé avec des odds ratios ajustés (OR) de 1,40 pour l’anxiété, 1,38 pour la dépression et 2,32 pour le stress. Les hommes recevant un traitement médicamenteux contre l’infertilité présentaient un risque plus élevé de symptômes d’anxiété (OR ajusté, 1,31) et de dépression (OR ajusté, 1,28), alors que ceux dont le traitement consistait à faire des inséminations intra-utérines présentaient un risque plus faible de symptômes d’anxiété (OR ajusté, 0,56) et de dépression (OR ajusté, 0,55). CONCLUSIONS: La pandémie de COVID-19 a eu un impact psychologique important sur les hommes infertiles. Plusieurs populations psychologiquement vulnérables ont été identifiées, notamment les personnes souffrant de dysfonction sexuelle, les hommes recevant un traitement médicamenteux contre l’infertilité, et ceux subissant des mesures de contrôle de la COVID-19. Les résultats fournissent un profil complet de l’état de santé mentale des hommes Chinois infertiles pendant l’épidémie de COVID-19 et fournissent des stratégies potentielles d’intervention psychologique.
Keywords: COVID-19; Male infertility; Psychological health; Sexual function.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevalence of and Risk Factors Associated With Mental Health Symptoms Among the General Population in China During the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic.JAMA Netw Open. 2020 Jul 1;3(7):e2014053. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.14053. JAMA Netw Open. 2020. PMID: 32609353 Free PMC article.
-
Immediate Psychological Responses and Associated Factors during the Initial Stage of the 2019 Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Epidemic among the General Population in China.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Mar 6;17(5):1729. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17051729. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32155789 Free PMC article.
-
The psychological impact of COVID-19 pandemic on the general population of Saudi Arabia.Compr Psychiatry. 2020 Oct;102:152192. doi: 10.1016/j.comppsych.2020.152192. Epub 2020 Jul 12. Compr Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32688022 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and associated factors of erectile dysfunction, psychological disorders, and sexual performance in primary vs. secondary infertility men.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2021 Mar 9;19(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s12958-021-00720-5. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2021. PMID: 33750412 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment on Occurrences of Depression and Anxiety and Associated Risk Factors in the Infertile Chinese Men.Am J Mens Health. 2017 May;11(3):767-774. doi: 10.1177/1557988317695901. Epub 2017 Feb 1. Am J Mens Health. 2017. PMID: 28413943 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Psychological impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on infertile patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Psych J. 2024 Oct;13(5):701-716. doi: 10.1002/pchj.782. Epub 2024 Jun 18. Psych J. 2024. PMID: 38894564 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic. 2021 [Available from: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources