Design of the Building Research in CRC prevention (BRIDGE-CRC) trial: a 6-month, parallel group Mediterranean diet and weight loss randomized controlled lifestyle intervention targeting the bile acid-gut microbiome axis to reduce colorectal cancer risk among African American/Black adults with obesity
- PMID: 36793105
- PMCID: PMC9930092
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-023-07115-4
Design of the Building Research in CRC prevention (BRIDGE-CRC) trial: a 6-month, parallel group Mediterranean diet and weight loss randomized controlled lifestyle intervention targeting the bile acid-gut microbiome axis to reduce colorectal cancer risk among African American/Black adults with obesity
Abstract
Background: Among all racial/ethnic groups, people who identify as African American/Blacks have the second highest colorectal cancer (CRC) incidence in the USA. This disparity may exist because African American/Blacks, compared to other racial/ethnic groups, have a higher prevalence of risk factors for CRC, including obesity, low fiber consumption, and higher intakes of fat and animal protein. One unexplored, underlying mechanism of this relationship is the bile acid-gut microbiome axis. High saturated fat, low fiber diets, and obesity lead to increases in tumor promoting secondary bile acids. Diets high in fiber, such as a Mediterranean diet, and intentional weight loss may reduce CRC risk by modulating the bile acid-gut microbiome axis. The purpose of this study is to test the impact of a Mediterranean diet alone, weight loss alone, or both, compared to typical diet controls on the bile acid-gut microbiome axis and CRC risk factors among African American/Blacks with obesity. Because weight loss or a Mediterranean diet alone can reduce CRC risk, we hypothesize that weight loss plus a Mediterranean diet will reduce CRC risk the most.
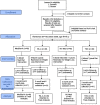
Methods: This randomized controlled lifestyle intervention will randomize 192 African American/Blacks with obesity, aged 45-75 years to one of four arms: Mediterranean diet, weight loss, weight loss plus Mediterranean diet, or typical diet controls, for 6 months (48 per arm). Data will be collected at baseline, mid-study, and study end. Primary outcomes include total circulating and fecal bile acids, taurine-conjugated bile acids, and deoxycholic acid. Secondary outcomes include body weight, body composition, dietary change, physical activity, metabolic risk, circulating cytokines, gut microbial community structure and composition, fecal short-chain fatty acids, and expression levels of genes from exfoliated intestinal cells linked to carcinogenesis.
Discussion: This study will be the first randomized controlled trial to examine the effects of a Mediterranean diet, weight loss, or both on bile acid metabolism, the gut microbiome, and intestinal epithelial genes associated with carcinogenesis. This approach to CRC risk reduction may be especially important among African American/Blacks given their higher risk factor profile and increased CRC incidence.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04753359 . Registered on 15 February 2021.
Keywords: Bile acids; Cancer health disparities; Colorectal cancer; Gut microbiome; Mediterranean diet; Nutrition; Weight loss.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Similar articles
-
Effects of a chronotype-adapted diet on weight loss, cardiometabolic health, and gut microbiota: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2024 Feb 28;25(1):152. doi: 10.1186/s13063-024-07996-z. Trials. 2024. PMID: 38419068 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between Diet, the Gut Microbiome, and Short-Chain Fatty Acid Production among Older Caribbean Latino Adults.J Acad Nutr Diet. 2020 Dec;120(12):2047-2060.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jand.2020.04.018. Epub 2020 Aug 12. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2020. PMID: 32798072
-
The effects of the Green-Mediterranean diet on cardiometabolic health are linked to gut microbiome modifications: a randomized controlled trial.Genome Med. 2022 Mar 10;14(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s13073-022-01015-z. Genome Med. 2022. PMID: 35264213 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dietary fat, bile acid metabolism and colorectal cancer.Semin Cancer Biol. 2021 Aug;73:347-355. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.10.003. Epub 2020 Oct 16. Semin Cancer Biol. 2021. PMID: 33069873 Review.
-
Fiber, Fat, and Colorectal Cancer: New Insight into Modifiable Dietary Risk Factors.Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2019 Dec 2;21(11):62. doi: 10.1007/s11894-019-0725-2. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31792624 Review.
Cited by
-
Melanoma and microbiota: Current understanding and future directions.Cancer Cell. 2024 Jan 8;42(1):16-34. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2023.12.003. Epub 2023 Dec 28. Cancer Cell. 2024. PMID: 38157864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ChatGPT-4o for Weight Management: Comparison of Different Diet Models.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Jul 16;13(7):e70639. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.70639. eCollection 2025 Jul. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40678335 Free PMC article.
-
Gut microbiota in colorectal cancer: a review of its influence on tumor immune surveillance and therapeutic response.Front Oncol. 2025 Mar 5;15:1557959. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1557959. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40110192 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulating Gut Microbiota with Dietary Components: A Novel Strategy for Cancer-Depression Comorbidity Management.Nutrients. 2025 Apr 29;17(9):1505. doi: 10.3390/nu17091505. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40362814 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High leafy and root vegetables and high rice dietary patterns were associated with primary and secondary bile acid levels in the feces.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 15;15(1):2092. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-86273-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39814946 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Cancer Society . Cancer Facts & Figures 2022. 2022.
-
- World Cancer Research Fund/American Institute for Cancer Research. The Continuous Update Project Expert Report 2018. Diet, nutrition, physical activity and colorectal cancer. Contin Updat Proj. 2018:1–62.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical