Quantitative evaluation of the reduction of distortion and metallic artifacts in magnetic resonance images using the multiacquisition variable‑resonance image combination selective sequence
- PMID: 36793326
- PMCID: PMC9922940
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2023.11808
Quantitative evaluation of the reduction of distortion and metallic artifacts in magnetic resonance images using the multiacquisition variable‑resonance image combination selective sequence
Abstract
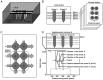
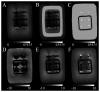
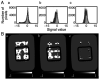
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is superior to computed tomography (CT) in determining changes in tissue structure, such as those observed following inflammation and infection. However, when metal implants or other metal objects are present, MRI exhibits more distortion and artifacts compared with CT, which hinders the accurate measurement of the implants. A limited number of reports have examined whether the novel MRI sequence, multiacquisition variable-resonance image combination selective (MAVRIC SL), can accurately measure metal implants without distortion. Therefore, the present study aimed to demonstrate whether MAVRIC SL could accurately measure metal implants without distortion and whether the area around the metal implants could be well delineated without artifacts. An agar phantom containing a titanium alloy lumbar implant was used for the present study and was imaged using a 3.0 T MRI machine. A total of three imaging sequences, namely MAVRIC SL, CUBE and magnetic image compilation (MAGiC), were applied and the results were compared. Distortion was evaluated by measuring the screw diameter and distance between the screws multiple times in the phase and frequency directions by two different investigators. The artifact region around the implant was examined using a quantitative method following standardization of the phantom signal values. It was revealed that MAVRIC SL was a superior sequence compared with CUBE and MAGiC, as there was significantly less distortion, a lack of bias between the two different investigators and significantly reduced artifact regions. These results suggested the possibility of utilizing MAVRIC SL for follow-up to observe metal implant insertions.
Keywords: MAVRIC SL; MRI; implant; metal artifacts; phantom.
Copyright: © Hirano et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
