Associations of Tissue Tumor Mutational Burden and Mutational Status With Clinical Outcomes With Pembrolizumab Plus Chemotherapy Versus Chemotherapy For Metastatic NSCLC
- PMID: 36793385
- PMCID: PMC9923193
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtocrr.2022.100431
Associations of Tissue Tumor Mutational Burden and Mutational Status With Clinical Outcomes With Pembrolizumab Plus Chemotherapy Versus Chemotherapy For Metastatic NSCLC
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Associations of Tissue Tumor Mutational Burden and Mutational Status With Clinical Outcomes With Pembrolizumab Plus Chemotherapy Versus Chemotherapy For Metastatic NSCLC [JTO Clinical and Research Reports Vol. 4 No. 1: 100431].JTO Clin Res Rep. 2025 Sep 2;6(10):100892. doi: 10.1016/j.jtocrr.2025.100892. eCollection 2025 Oct. JTO Clin Res Rep. 2025. PMID: 41089738 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Introduction: We evaluated tissue tumor mutational burden (tTMB) and mutations in STK11, KEAP1, and KRAS as biomarkers for outcomes with pembrolizumab plus platinum-based chemotherapy (pembrolizumab-combination) for NSCLC among patients in the phase 3 KEYNOTE-189 (ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT02578680; nonsquamous) and KEYNOTE-407 (ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT02775435; squamous) trials.
Methods: This retrospective exploratory analysis evaluated prevalence of high tTMB and STK11, KEAP1, and KRAS mutations in patients enrolled in KEYNOTE-189 and KEYNOTE-407 and the relationship between these potential biomarkers and clinical outcomes. tTMB and STK11, KEAP1, and KRAS mutation status was assessed using whole-exome sequencing in patients with available tumor and matched normal DNA. The clinical utility of tTMB was assessed using a prespecified cutpoint of 175 mutations/exome.
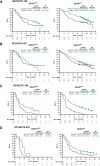
Results: Among patients with evaluable data from whole-exome sequencing for evaluation of tTMB (KEYNOTE-189, n = 293; KEYNOTE-407, n = 312) and matched normal DNA, no association was found between continuous tTMB score and overall survival (OS) or progression-free survival for pembrolizumab-combination (Wald test, one-sided p > 0.05) or placebo-combination (Wald test, two-sided p > 0.05) in patients with squamous or nonsquamous histology. Pembrolizumab-combination improved outcomes for patients with tTMB greater than or equal to 175 compared with tTMB less than 175 mutations/exome in KEYNOTE-189 (OS, hazard ratio = 0.64 [95% confidence interval (CI): 0.38‒1.07] and 0.64 [95% CI: 0.42‒0.97], respectively) and KEYNOTE-407 (OS, hazard ratio = 0.74 [95% CI: 0.50‒1.08 and 0.86 [95% CI: 0.57‒1.28], respectively) versus placebo-combination. Treatment outcomes were similar regardless of KEAP1, STK11, or KRAS mutation status.
Conclusions: These findings support pembrolizumab-combination as first-line treatment in patients with metastatic NSCLC and do not suggest the utility of tTMB, STK11, KEAP1, or KRAS mutation status as a biomarker for this regimen.
Keywords: Biomarker; Metastatic non‒small-cell lung cancer; Pembrolizumab; Single-gene genetic alterations; Tissue tumor mutational burden.
© 2022 The Authors.
Figures




References
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology [NCCN Guidelines]: non-small-cell lung cancer, version 3.2019. https://www.nccn.org/patients/guidelines/cancers.aspx#nsclc
-
- Planchard D., Popat S., Kerr K., et al. Metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2019;30:863–870. - PubMed
-
- Gandhi L., Rodriguez-Abreu D., Gadgeel S., et al. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:2078–2092. - PubMed
-
- Paz-Ares L., Luft A., Vicente D., et al. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy for squamous non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:2040–2051. - PubMed
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

