Syntheses and crystal structures of two di-naph-tho[2,1- d:1',2'- f][1,3]dithiepine atropisomers
- PMID: 36793408
- PMCID: PMC9912471
- DOI: 10.1107/S2056989023000476
Syntheses and crystal structures of two di-naph-tho[2,1- d:1',2'- f][1,3]dithiepine atropisomers
Abstract
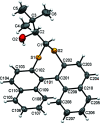
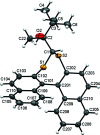
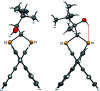
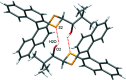
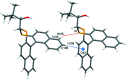
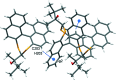
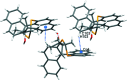
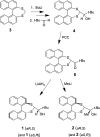
The closely related title compounds, 1-(di-naphtho-[2,1-d:1',2'-f][1,3]dithiepin-4-yl)-2,2-di-methyl-propan-1-ol, C26H24OS2, 1 and 2-(di-naphtho-[2,1-d:1',2'-f][1,3]dithiepin-4-yl)-3,3-di-methyl-butan-2-ol, C27H26OS2, 2, both comprise an atrop-isomeric binaphthyl di-thio-acetal unit substituted at the methyl-ene carbon atom with a chiral neopentyl alcohol grouping. The overall stereochemistry of the racemate in each case is defined as aS,R and aR,S. In 1, the hydroxyl group generates inversion dimers via pairwise inter-molecular O-H⋯S hydrogen bonds whereas in 2, the O-H⋯S link is intra-molecular. Weak C-H⋯π inter-actions link the mol-ecules into extended arrays in both structures.
Keywords: C—H⋯π contacts; asymmetric synthesis; atropisomer; binaphthalene dithiol; crystal structure; hydrogen bonds.
© Beare et al. 2023.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Syntheses and crystal structure of a (2,6-diiso-propyldi-naphtho-[2,1-d:1',2'-f][1,3]dithiepin-4-yl)(phen-yl)methanol atropisomer.Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2023 Feb 28;79(Pt 3):241-245. doi: 10.1107/S2056989023001706. eCollection 2023 Feb 1. Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2023. PMID: 36909995 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structures of the synthetic inter-mediate 3-[(6-chloro-7H-purin-7-yl)meth-yl]cyclo-butan-1-one, and of two oxetanocin derivatives: 3-[(6-chloro-8,9-di-hydro-7H-purin-7-yl)meth-yl]cyclo-butan-1-ol and 3-[(6-chloro-9H-purin-9-yl)meth-yl]cyclo-butan-1-ol.Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2019 May 3;75(Pt 6):732-737. doi: 10.1107/S2056989019004432. eCollection 2019 Jun 1. Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2019. PMID: 31391955 Free PMC article.
-
Bis(N,N-di-ethyl-dithio-carbamato-κ2S,S')(3-hy-droxy-pyridine-κN)zinc and bis-[N-(2-hy-droxy-eth-yl)-N-methyldithio-carbamato-κ2S,S'](3-hy-droxy-pyridine-κN)zinc: crystal structures and Hirshfeld surface analysis.Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2016 Nov 1;72(Pt 12):1700-1709. doi: 10.1107/S205698901601728X. eCollection 2016 Dec 1. Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2016. PMID: 27980812 Free PMC article.
-
(N,N-Di-allyl-dithio-carbamato-κ2 S,S')tri-phenyltin(IV) and bis-(N,N-di-allyl-dithio-carbamato-κ2 S,S')di-phenyl-tin(IV): crystal structure, Hirshfeld surface analysis and computational study.Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2020 Jan 10;76(Pt 2):167-176. doi: 10.1107/S2056989020000122. eCollection 2020 Feb 1. Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2020. PMID: 32071741 Free PMC article.
-
N-[(2,6-Di-ethyl-phen-yl)carbamo-thio-yl]-2,2-di-phenyl-acetamide.Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2013 May 25;69(Pt 6):o967. doi: 10.1107/S1600536813013354. Print 2013 Jun 1. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2013. PMID: 23795124 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Syntheses and crystal structure of a (2,6-diiso-propyldi-naphtho-[2,1-d:1',2'-f][1,3]dithiepin-4-yl)(phen-yl)methanol atropisomer.Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2023 Feb 28;79(Pt 3):241-245. doi: 10.1107/S2056989023001706. eCollection 2023 Feb 1. Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2023. PMID: 36909995 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bruker (1998). SMART and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Cheng, J. K., Xiang, S.-H., Li, S., Ye, L. & Tan, B. (2021). Chem. Rev. 121, 4805–4902. - PubMed
-
- Delogu, G., De Lucchi, O., Maglioli, P. & Valle, G. (1991). J. Org. Chem. 56, 4467–4473.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
