Discovery of Bis-sulfonamides as Novel Inhibitors of Mitochondrial NADH-Quinone Oxidoreductase (Complex I)
- PMID: 36793437
- PMCID: PMC9923842
- DOI: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.2c00504
Discovery of Bis-sulfonamides as Novel Inhibitors of Mitochondrial NADH-Quinone Oxidoreductase (Complex I)
Abstract
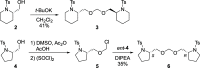
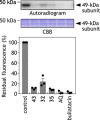
Mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) is an essential cellular metabolic process that generates ATP. The enzymes involved in OXPHOS are considered to be promising druggable targets. Through screening of an in-house synthetic library with bovine heart submitochondrial particles, we identified a unique symmetric bis-sulfonamide, KPYC01112 (1) as an inhibitor targeting NADH-quinone oxidoreductase (complex I). Structural modifications of KPYC01112 (1) led to the discovery of the more potent inhibitors 32 and 35 possessing long alkyl chains (IC50 = 0.017 and 0.014 μM, respectively). A photoaffinity labeling experiment using a newly synthesized photoreactive bis-sulfonamide ([125I]-43) revealed that it binds to the 49-kDa, PSST, and ND1 subunits which make up the quinone-accessing cavity of complex I.
© 2023 American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

