High frequency deep brain stimulation can mitigate the acute effects of cocaine administration on tonic dopamine levels in the rat nucleus accumbens
- PMID: 36793536
- PMCID: PMC9922701
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1061578
High frequency deep brain stimulation can mitigate the acute effects of cocaine administration on tonic dopamine levels in the rat nucleus accumbens
Abstract
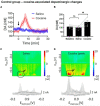
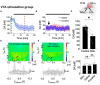
Cocaine's addictive properties stem from its capacity to increase tonic extracellular dopamine levels in the nucleus accumbens (NAc). The ventral tegmental area (VTA) is a principal source of NAc dopamine. To investigate how high frequency stimulation (HFS) of the rodent VTA or nucleus accumbens core (NAcc) modulates the acute effects of cocaine administration on NAcc tonic dopamine levels multiple-cyclic square wave voltammetry (M-CSWV) was used. VTA HFS alone decreased NAcc tonic dopamine levels by 42%. NAcc HFS alone resulted in an initial decrease in tonic dopamine levels followed by a return to baseline. VTA or NAcc HFS following cocaine administration prevented the cocaine-induced increase in NAcc tonic dopamine. The present results suggest a possible underlying mechanism of NAc deep brain stimulation (DBS) in the treatment of substance use disorders (SUDs) and the possibility of treating SUD by abolishing dopamine release elicited by cocaine and other drugs of abuse by DBS in VTA, although further studies with chronic addiction models are required to confirm that. Furthermore, we demonstrated the use of M-CSWV can reliably measure tonic dopamine levels in vivo with both drug administration and DBS with minimal artifacts.
Keywords: cocaine; deep brain stimulation; nucleus accumbens; substance use disorder; tonic dopamine; ventral tegmental area.
Copyright © 2023 Yuen, Goyal, Rusheen, Kouzani, Berk, Kim, Tye, Blaha, Bennet, Lee, Shin and Oh.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors andMayo Clinic have a Financial Conflict of Interest in technology used in the research and that the authors and Mayo Clinic may stand to gain financially from the successful outcome of the research.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Oxycodone-induced dopaminergic and respiratory effects are modulated by deep brain stimulation.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jun 20;14:1199655. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1199655. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37408764 Free PMC article.
-
Cocaine-Induced Changes in Tonic Dopamine Concentrations Measured Using Multiple-Cyclic Square Wave Voltammetry in vivo.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jul 6;12:705254. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.705254. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34295252 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-manic effect of deep brain stimulation of the ventral tegmental area in an animal model of mania induced by methamphetamine.Bipolar Disord. 2024 Jun;26(4):376-387. doi: 10.1111/bdi.13423. Epub 2024 Apr 1. Bipolar Disord. 2024. PMID: 38558302
-
Dopamine signaling in the nucleus accumbens of animals self-administering drugs of abuse.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2010;3:29-71. doi: 10.1007/7854_2009_27. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 21161749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dopamine D3 and 5-HT1B receptor dysregulation as a result of psychostimulant intake and forced abstinence: Implications for medications development.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Jan;76 Pt B(0 0):301-19. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.08.014. Epub 2013 Aug 23. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 23973315 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in Brain Stimulation, Nanomedicine and the Use of Magnetoelectric Nanoparticles: Dopaminergic Alterations and Their Role in Neurodegeneration and Drug Addiction.Molecules. 2024 Jul 29;29(15):3580. doi: 10.3390/molecules29153580. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39124985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resolution of tonic concentrations of highly similar neurotransmitters using voltammetry and deep learning.Mol Psychiatry. 2024 Oct;29(10):3076-3085. doi: 10.1038/s41380-024-02537-1. Epub 2024 Apr 25. Mol Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38664492 Free PMC article.
-
High-Frequency Stimulation of the Ventral Tegmental Area Rescues Respiratory Failure.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 23:rs.3.rs-6740056. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-6740056/v1. Res Sq. 2025. PMID: 40678236 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
AKAP150 from nucleus accumbens dopamine D1 and D2 receptor-expressing medium spiny neurons regulates morphine withdrawal.iScience. 2023 Oct 17;26(11):108227. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108227. eCollection 2023 Nov 17. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37953959 Free PMC article.
-
Oxycodone-induced dopaminergic and respiratory effects are modulated by deep brain stimulation.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jun 20;14:1199655. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1199655. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37408764 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baldermann J. C., Schuller T., Huys D., Becker I., Timmermann L., Jessen F., et al. (2016). Deep brain stimulation for tourette-syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain Stimul. 9 296–304. - PubMed
-
- Bass C. E., Grinevich V. P., Gioia D., Day-Brown J. D., Bonin K. D., Stuber G. D., et al. (2013). Optogenetic stimulation of VTA dopamine neurons reveals that tonic but not phasic patterns of dopamine transmission reduce ethanol self-administration. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 7:173. 10.3389/fnbeh.2013.00173 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

