Protective role of colitis in inflammatory arthritis via propionate-producing Bacteroides in the gut
- PMID: 36793721
- PMCID: PMC9923108
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1064900
Protective role of colitis in inflammatory arthritis via propionate-producing Bacteroides in the gut
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate whether and how inflammatory disease in the intestine influences the development of arthritis, considering that organ-to-organ communication is associated with many physiological and pathological events.
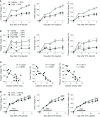
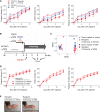
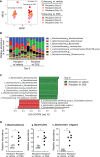
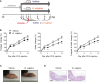
Methods: First, mice were given drinking water containing dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) and then subjected to inflammatory arthritis. We compared the phenotypic symptoms between the cohoused and separately-housed mice. Next, donor mice were divided into DSS-treated and untreated groups and then cohoused with recipient mice. Arthritis was then induced in the recipients. The fecal microbiome was analyzed by 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing. We obtained type strains of the candidate bacteria and generated propionate-deficient mutant bacteria. Short-chain fatty acids were measured in the bacterial culture supernatant, serum, feces, and cecum contents using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Mice fed with candidate and mutant bacteria were subjected to inflammatory arthritis.
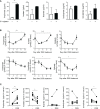
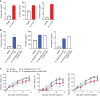
Results: Contrary to expectations, the mice treated with DSS exhibited fewer symptoms of inflammatory arthritis. Intriguingly, the gut microbiota contributes, at least in part, to the improvement of colitis-mediated arthritis. Among the altered microorganisms, Bacteroides vulgatus and its higher taxonomic ranks were enriched in the DSS-treated mice. B. vulgatus, B. caccae, and B. thetaiotaomicron exerted anti-arthritic effects. Propionate production deficiency further prevented the protective effect of B. thetaiotaomicron on arthritis.
Conclusions: We suggest a novel relationship between the gut and joints and an important role of the gut microbiota as communicators. Moreover, the propionate-producing Bacteroides species examined in this study may be a potential candidate for developing effective treatments for inflammatory arthritis.
Keywords: Bacteroides; arthritis; colitis; gut microbiota; propionate.
Copyright © 2023 Shon, Kim, Kim, Choi, Cho, An, Park, Cho, Park, Seo, Cho, Kim and Kim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii served as key components of fecal microbiota transplantation to alleviate colitis.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2024 May 1;326(5):G607-G621. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00303.2023. Epub 2024 Mar 19. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38502145 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of cinnamon essential oil on gut microbiota in the mouse model of dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis.Microbiol Immunol. 2020 Jan;64(1):23-32. doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.12749. Epub 2019 Nov 26. Microbiol Immunol. 2020. PMID: 31595527
-
Effects of IRW and IQW on Oxidative Stress and Gut Microbiota in Dextran Sodium Sulfate-Induced Colitis.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;51(1):441-451. doi: 10.1159/000495240. Epub 2018 Nov 19. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30453297
-
Effects of Pretreatment with Bifidobacterium bifidum Using 16S Ribosomal RNA Gene Sequencing in a Mouse Model of Acute Colitis Induced by Dextran Sulfate Sodium.Med Sci Monit. 2021 Mar 9;27:e928478. doi: 10.12659/MSM.928478. Med Sci Monit. 2021. PMID: 33686049 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-Like Receptor 7 Agonist-Induced Dermatitis Causes Severe Dextran Sulfate Sodium Colitis by Altering the Gut Microbiome and Immune Cells.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Sep 25;7(1):135-156. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2018.09.010. eCollection 2019. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 30510995 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Impact of Cannabidiol and Exercise on Clinical Outcomes and Gut Microbiota for Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Cancer Survivors: A Case Report.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jun 25;17(7):834. doi: 10.3390/ph17070834. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39065685 Free PMC article.
-
Bacillus subtilis (NMCC-path-14) ameliorates acute phase of arthritis via modulating NF-κB and Nrf-2 signaling in mice model.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 Apr;33(4):1863-1877. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01676-3. Epub 2025 Feb 26. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40009344
-
Microbiota and metabolome dynamics induced by Shiga toxin-producing E. coli in an in vitro model of an infant's colon.Microb Cell. 2025 Apr 14;12:76-92. doi: 10.15698/mic2025.04.847. eCollection 2025. Microb Cell. 2025. PMID: 40309356 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Fiber Inulin Improves Murine Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-like Dermatitis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 17;24(18):14197. doi: 10.3390/ijms241814197. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762500 Free PMC article.
-
Gut microbiota and blood biomarkers in IBD-Related arthritis: insights from mendelian randomization.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 2;15(1):514. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-84116-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39747467 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

