Multi-parametric MRI without artificial erection for preoperative assessment of primary penile carcinoma: A pilot study on the correlation between imaging and histopathological findings
- PMID: 36793771
- PMCID: PMC9922909
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejro.2023.100478
Multi-parametric MRI without artificial erection for preoperative assessment of primary penile carcinoma: A pilot study on the correlation between imaging and histopathological findings
Abstract
Purpose: We aimed to evaluate the diagnostic potential of non-erectile multi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging (mpMRI) for preoperative assessment of primary penile squamous cell carcinoma (SCC).
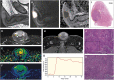
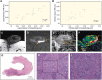
Method: Twenty-five patients who underwent surgery for penile SCC were included. Preoperative mpMRI without artificial erection was performed in all patients. The preoperative MRI protocol consisted of high-resolution morphological and functional sequences (diffusion-weighted imaging and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI perfusion) covering the penis and lower pelvis. T and N staging, according to the 8th edition of the Union for International Cancer Control TNM classification, as well as the largest diameter and thickness/infiltration depth of the primary lesions were determined in all patients. Imaging data were retrospectively collected and compared with the final histopathology reports.
Results: Very good agreement was observed between MRI and histopathology for the involvement of corpus spongiosum (p = 0.002) and good agreement was observed for the involvement of penile urethra and tunica albuginea/corpus cavernosum (p < 0.001 and p = 0.007, respectively). Good agreement was observed between MRI and histopathology for overall T staging and weaker, but still good agreement was observed for N staging (p < 0.001 and p = 0.002, respectively). A strong and significant correlation was observed between MRI and histopathology for the largest diameter and thickness/infiltration depth of the primary lesions (p < 0.001).
Conclusions: Good concordance was observed between MRI and histopathological findings. Our initial findings indicate that non-erectile mpMRI is useful in preoperative assessment of primary penile SCC.
Keywords: Histopathology; Multi-parametric MRI; Primary penile carcinoma; Surgery.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Hanchanale V., Yeo L., Subedi N., Smith J., Wah T., Harnden P., Bhattarai S., Chilka S., Eardley I. The accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in predicting the invasion of the tunica albuginea and the urethra during the primary staging of penile cancer. BJU Int. 2016;117(3):439–443. - PubMed
-
- Cubilla A.L., Barreto J., Caballero C., Ayala G., Riveros M. Pathologic features of epidermoid carcinoma of the penis. A prospective study of 66 cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1993;17(8):753–763. - PubMed
-
- Kieffer J.M., Djajadiningrat R.S., van Muilekom E.A., Graafland N.M., Horenblas S., Aaronson N.K. Quality of life for patients treated for penile cancer. J. Urol. 2014;192(4):1105–1110. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

