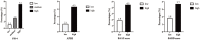The association between liver fibrosis scores and chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 36793875
- PMCID: PMC9922852
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1046825
The association between liver fibrosis scores and chronic kidney disease
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to clarify the relationship between liver fibrosis scores (Fibrosis-4, BARD score, and BAAT score) and chronic kidney disease (CKD).
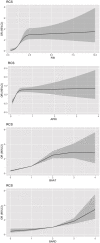
Methods: We collected a range of data from 11,503 subjects (5,326 men and 6,177 women) from the rural regions of Northeastern China. Three liver fibrosis scores (LFSs) including fibrosis-4 (FIB-4), BARD score, and BAAT score were adopted. A logistic regression analysis was used to calculate odds ratios and the 95% confidence interval. A subgroup analysis showed the association between LFSs and CKD under different stratifications. Restricted cubic spline could further explore whether there is a linear relationship between LFSs and CKD. Finally, we used C-statistics, Net Reclassification Index (NRI), and Integrated Discrimination Improvement (IDI) to assess the effect of each LFS on CKD.
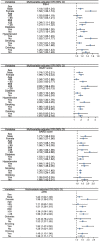
Results: Through the baseline characteristics, we observed that LFSs were higher in the CKD population than in non-CKD. The proportion of participants with CKD also increased with LFSs. In a multivariate logistic regression analysis, the ORs of CKD were 6.71 (4.45-10.13) in FIB-4, 1.88 (1.29-2.75) in the BAAT score, and 1.72 (1.28-2.31) in the BARD score by comparing the high level with the low level in each LFSs. Moreover, after adding LFSs to the original risk prediction model, which consisted of age, sex, drinking, smoking, diabetes, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, total cholesterol, triglycerides, and mean waist circumference, we found the new models have higher C-statistics. Furthermore, NRI and IDI both indicate LFSs had a positive effect on the model.
Conclusions: Our study showed that LFSs are associated with CKD among middle-aged populations in rural areas of northeastern China.
Keywords: BAAT score; BARD score; chronic kidney disease; fibrosis-4; liver fibrosis scores.
Copyright © 2023 Xiong, Wang, Yin, Deng, Zhao, Li, Li, Zhou, Yu, Yang, Guo and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of liver fibrosis score on the incidence of stroke: A cohort study.Liver Int. 2022 Oct;42(10):2175-2185. doi: 10.1111/liv.15359. Epub 2022 Jul 16. Liver Int. 2022. PMID: 35789194
-
Predictive value of liver fibrosis scores in cardiovascular diseases among hypertensive population.J Hypertens. 2023 May 1;41(5):741-750. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000003394. Epub 2023 Mar 20. J Hypertens. 2023. PMID: 36883472 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Invasive Liver Fibrosis Scores Are Associated With Contrast-Associated Acute Kidney Injury in Patients Undergoing Elective Percutaneous Coronary Intervention.Angiology. 2023 Apr;74(4):333-343. doi: 10.1177/00033197221105745. Epub 2022 May 31. Angiology. 2023. PMID: 35642134
-
Comparison of liver fibrosis scores for predicting mortality and morbidity in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.ESC Heart Fail. 2023 Jun;10(3):1771-1780. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14336. Epub 2023 Mar 2. ESC Heart Fail. 2023. PMID: 36864701 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of FIB-4 index, NAFLD fibrosis score and BARD score for prediction of advanced fibrosis in adult patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A meta-analysis study.Hepatol Res. 2016 Aug;46(9):862-70. doi: 10.1111/hepr.12647. Epub 2016 Feb 16. Hepatol Res. 2016. PMID: 26763834 Review.
Cited by
-
The association of liver fibrosis and chronic kidney disease in patients with metabolic associated fatty liver disease: A cross-sectional study.Saudi Med J. 2024 Oct;45(10):1034-1040. doi: 10.15537/smj.2024.45.10.20240393. Saudi Med J. 2024. PMID: 39379109 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources