Cytochrome P450 3A4 suppression by epimedium and active compound kaempferol leads to synergistic anti-inflammatory effect with corticosteroid
- PMID: 36793921
- PMCID: PMC9922998
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1042756
Cytochrome P450 3A4 suppression by epimedium and active compound kaempferol leads to synergistic anti-inflammatory effect with corticosteroid
Abstract
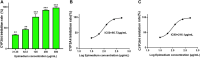
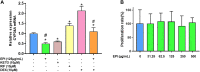
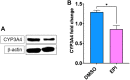
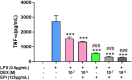
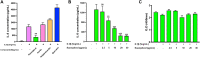
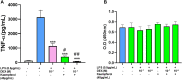
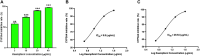
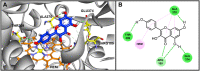
Introduction: Cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A4 is a major drug metabolizing enzyme for corticosteroids (CS). Epimedium has been used for asthma and variety of inflammatory conditions with or without CS. It is unknown whether epimedium has an effect on CYP 3A4 and how it interacts with CS. We sought to determine the effects of epimedium on CYP3A4 and whether it affects the anti-inflammatory function of CS and identify the active compound responsible for this effect. Methods: The effect of epimedium on CYP3A4 activity was evaluated using the Vivid CYP high-throughput screening kit. CYP3A4 mRNA expression was determined in human hepatocyte carcinoma (HepG2) cells with or without epimedium, dexamethasone, rifampin, and ketoconazole. TNF-α levels were determined following co-culture of epimedium with dexamethasone in a murine macrophage cell line (Raw 264.7). Active compound (s) derived from epimedium were tested on IL-8 and TNF-α production with or without corticosteroid, on CYP3A4 function and binding affinity. Results: Epimedium inhibited CYP3A4 activity in a dose-dependent manner. Dexamethasone enhanced the expression of CYP3A4 mRNA, while epimedium inhibited the expression of CYP3A4 mRNA and further suppressed dexamethasone enhancement of CYP3A4 mRNA expression in HepG2 cells (p < 0.05). Epimedium and dexamethasone synergistically suppressed TNF-α production by RAW cells (p < 0.001). Eleven epimedium compounds were screened by TCMSP. Among the compounds identified and tested only kaempferol significantly inhibited IL-8 production in a dose dependent manner without any cell cytotoxicity (p < 0.01). Kaempferol in combination with dexamethasone showed complete elimination of TNF-α production (p < 0.001). Furthermore, kaempferol showed a dose dependent inhibition of CYP3A4 activity. Computer docking analysis showed that kaempferol significantly inhibited the catalytic activity of CYP3A4 with a binding affinity of -44.73kJ/mol. Discussion: Inhibition of CYP3A4 function by epimedium and its active compound kaempferol leads to enhancement of CS anti-inflammatory effect.
Keywords: CYP3A4; anti-inflammation; drug-drug interaction (DDI); epimedium; kaempferol.
Copyright © 2023 Li, Yu, Maskey, Musa, Wang, Garcia, Guo, Yang, Srivastava, Dunkin, Li, Guo, Cheng, Yuan, Tiwari and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
X-ML received research support to her institution from the National Institutes of Health (NIH)/National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine (NCCAM) # 1P01 AT002644725-01 “Center for Chinese Herbal Therapy (CHT) for Asthma”, and grant #1R01AT001495-01A1 and 2R01 AT001495-05A2, NIH/NIAID R43AI148039, Food Allergy Research and Education (FARE), Winston Wolkoff Integrative Medicine Fund for Allergies and Wellness, the Parker Foundation and Henan University of Chinese Medicine; received consultancy fees from FARE and Johnson & Johnson Pharmaceutical Research & Development, L.L.C. Bayer Global Health LLC; received royalties from Up To Date; is an Honorary Professor of Chinese Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan; Henan University of Chinese Medicine Zhenzhou, China, and Professorial Lecture at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, US; received travel expenses from the NCCAM and FARE; share US patent US7820175B2 (FAHF-2), US10500169B2 (XPP), US10406191B2 (S. Flavescens), US10028985B2 (WL); US11351157B2 (nanoBBR): take compensation from her practice at Center for Integrative Health and Acupuncture PC; US Times Technology Inc is managed by her related party; is a member of General Nutraceutical Technology LLC and Health Freedom LLC.Nan Yang received research support from the National Institutes of Health (NIH)/National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine (NCCAM), NIH/NIAID R43AI148039; shares US patent: US10500169B2 (XPP), US10406191B2 (S. Flavescens), US10028985B2 (WL); and is a member of General Nutraceutical Technology LLC and Health Freedom LLC. Kamal Srivastava share PCT/US2017/056822. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- de Vries J. H., Hollman P. C., Meyboom S., Buysman M. N., Zock P. L., van Staveren W. A., et al. (1998). Plasma concentrations and urinary excretion of the antioxidant flavonols quercetin and kaempferol as biomarkers for dietary intake. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 68 (1), 60–65. 10.1093/ajcn/68.1.60 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

