Equisetum arvense Inhibits Alveolar Bone Destruction in a Rat Model with Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Periodontitis
- PMID: 36794024
- PMCID: PMC9925265
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/7398924
Equisetum arvense Inhibits Alveolar Bone Destruction in a Rat Model with Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Periodontitis
Abstract
Background and aims: Equisetum arvense extract (EA) exerts various biological effects, including anti-inflammatory activity. The effect of EA on alveolar bone destruction has not been reported; therefore, we aimed to determine whether EA could inhibit alveolar bone destruction associated with periodontitis in a rat model in which periodontitis was induced using lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli (E. coli-LPS).
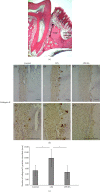
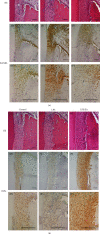
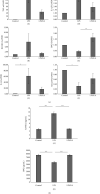
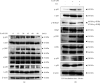
Methods: Physiological saline or E. coli-LPS or E. coli-LPS/EA mixture was topically administered into the gingival sulcus of the upper molar region of the rats. After 3 days, periodontal tissues of the molar region were collected. Immunohistochemistry was performed for cathepsin K, receptor activator of NF-κB ligand (RANKL), and osteoprotegerin (OPG). The cathepsin K-positive osteoclasts along the alveolar bone margin were counted. EA effects on the expression of the factors regulating osteoclastogenesis in osteoblasts with E. coli-LPS-stimulation were also examined in vitro.
Results: Treatment with EA significantly reduced the number of osteoclasts by decreasing the RANKL-expression and increasing OPG-expression in the periodontal ligament in the treatment group compared to the E. coli-LPS group. The in vitro study showed that the upregulation of p-IκB kinase α and β (p-IKKα/β), p-NF-κB p65, TNF-α, interleukin-6, and RANKL and downregulation of semaphorin 3A (Sema3A), β-catenin, and OPG in the osteoblasts with E. coli-LPS-stimulation improved with EA-treatment.
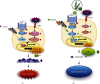
Conclusion: These findings demonstrated that topical EA suppressed alveolar bone resorption in the rat model with E. coli-LPS-induced periodontitis by maintaining a balance in RANKL/OPG ratio via the pathways of NF-κB, Wnt/β-catenin, and Sema3A/Neuropilin-1. Therefore, EA possesses the potential to prevent bone destruction through inhibiting osteoclastogenesis attributed to cytokine burst under plaque accumulation.
Copyright © 2022 Fumie Shiba et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inhibitory effects of orally administrated liposomal bovine lactoferrin on the LPS-induced osteoclastogenesis.Lab Invest. 2010 Aug;90(8):1236-46. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2010.80. Epub 2010 Apr 26. Lab Invest. 2010. PMID: 20421871
-
Oral administration of prostaglandin E(2)-specific receptor 4 antagonist inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced osteoclastogenesis in rat periodontal tissue.J Periodontol. 2012 Apr;83(4):506-13. doi: 10.1902/jop.2011.110301. Epub 2011 Sep 12. J Periodontol. 2012. PMID: 21910594
-
Effects of novel lactoferrin peptides on LPS-induced alveolar bone destruction in a rat model.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2024 Jul;104(1):e14574. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.14574. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2024. PMID: 38958121
-
Immune response: the key to bone resorption in periodontal disease.J Periodontol. 2005 Nov;76(11 Suppl):2033-41. doi: 10.1902/jop.2005.76.11-S.2033. J Periodontol. 2005. PMID: 16277573 Review.
-
The RANKL-OPG system in clinical periodontology.J Clin Periodontol. 2012 Mar;39(3):239-48. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2011.01810.x. Epub 2011 Oct 24. J Clin Periodontol. 2012. PMID: 22092994 Review.
Cited by
-
Semaphorin 3A on Osteoporosis: An Overreview of the Literature.Calcif Tissue Int. 2025 Feb 22;116(1):43. doi: 10.1007/s00223-025-01350-4. Calcif Tissue Int. 2025. PMID: 39985619 Review.
-
[Research Advances in the Replication of Animal Models for Periodontal Diseases].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025 Mar 20;56(2):339-344. doi: 10.12182/20250360103. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025. PMID: 40599292 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of Equisetum arvense L. on acid-induced ulcerative colitis in rats.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 21;15(1):13727. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-97693-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40258911 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemical Investigation of Equisetum arvense and Evaluation of Their Anti-Inflammatory Potential in TNFα/INFγ-Stimulated Keratinocytes.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Oct 16;16(10):1478. doi: 10.3390/ph16101478. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37895949 Free PMC article.
-
Antinociceptive effect of Equisetum arvense extract on the stomatitis hamster model.PLoS One. 2024 Nov 21;19(11):e0313747. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0313747. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39570913 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang H. y, Qin H. x, Deng H., Sun C. f, Hu R. d. Effects of LPS-stimulated monocyte culture supernatant on the OPG/RANKL of osteoblastic cells. Shanghai Journal of Stomatology . 2015;24(4):428–432. - PubMed
-
- Chuang F. H., Tsai C. C., Chen J. H., Chen K. K., Chen Y. K., Lin Y. C. Long-term sequential receptor activator of NF-κB ligand (RANKL) and osteoprotegrin (OPG) expression in lipopolysaccharide-induced rat periapical lesions. Journal of Oral Pathology & Medicine . 2012;41(2):186–193. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.2011.01065.x. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

