Describing epilepsy-related anxiety to inform the design of a virtual reality exposure therapy: Results from Phase 1 of the AnxEpiVR clinical trial
- PMID: 36794093
- PMCID: PMC9922786
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebr.2023.100588
Describing epilepsy-related anxiety to inform the design of a virtual reality exposure therapy: Results from Phase 1 of the AnxEpiVR clinical trial
Abstract
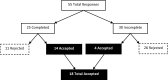
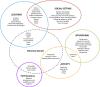
People with epilepsy (PwE) are at a greater risk of comorbid anxiety, which is often related to the fear of having another seizure for safety or social reasons. While virtual reality (VR) exposure therapy (ET) has been successfully used to treat several anxiety disorders, no studies to date have investigated its use in this population. This paper discusses Phase 1 of the three-phase AnxEpiVR pilot study. In Phase 1, we aimed to explore and validate scenarios that provoke epilepsy/seizure-specific (ES) interictal anxiety and provide recommendations that lay the foundation for designing VR-ET scenarios to treat this condition in PwE. An anonymous online questionnaire (including open- and closed-ended questions) that targeted PwE and those affected by it (e.g., through a family member, friend, or as a healthcare professional) was promoted by a major epilepsy foundation in Toronto, Canada. Responses from n = 18 participants were analyzed using grounded theory and the constant comparison method. Participants described anxiety-provoking scenes, which were categorized under the following themes: location, social setting, situational, activity, physiological, and previous seizure. While scenes tied to previous seizures were typically highly personalized and idiosyncratic, public settings and social situations were commonly reported fears. Factors consistently found to increase ES-interictal anxiety included the potential for danger (physical injury or inability to get help), social factors (increased number of unfamiliar people, social pressures), and specific triggers (stress, sensory, physiological, and medication-related). We make recommendations for incorporating different combinations of anxiety-related factors to achieve a customizable selection of graded exposure scenarios suitable for VR-ET. Subsequent phases of this study will include creating a set of VR-ET hierarchies (Phase 2) and rigorously evaluating their feasibility and effectiveness (Phase 3).
Keywords: Anxiety; Cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT); Epilepsy; Exposure therapy; Non-pharmacological intervention; Virtual reality.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Kerr M.P. The impact of epilepsy on patients’ lives. Acta Neurol Scand. 2012;126(s194):1–9. - PubMed
-
- Ertan D., Hubert-Jacquot C., Maillard L., Sanchez S., Jansen C., Fracomme L., et al. Anticipatory anxiety of epileptic seizures: An overlooked dimension linked to trauma history. Seizure - Eur J Epilepsy. 2021;1(85):64–69. - PubMed
-
- Hingray C., McGonigal A., Kotwas I., Micoulaud-Franchi J.A. The Relationship Between Epilepsy and Anxiety Disorders. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2019;21(6):40. - PubMed
-
- Mula M. Treatment of anxiety disorders in epilepsy: An evidence-based approach. Epilepsia. 2013;54(s1):13–18. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical