A Novel Framework for Melanoma Lesion Segmentation Using Multiparallel Depthwise Separable and Dilated Convolutions with Swish Activations
- PMID: 36794097
- PMCID: PMC9925248
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/1847115
A Novel Framework for Melanoma Lesion Segmentation Using Multiparallel Depthwise Separable and Dilated Convolutions with Swish Activations
Abstract
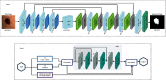
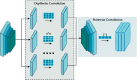
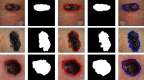
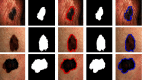
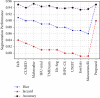
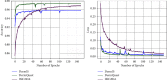
Skin cancer remains one of the deadliest kinds of cancer, with a survival rate of about 18-20%. Early diagnosis and segmentation of the most lethal kind of cancer, melanoma, is a challenging and critical task. To diagnose medicinal conditions of melanoma lesions, different researchers proposed automatic and traditional approaches to accurately segment the lesions. However, visual similarity among lesions and intraclass differences are very high, which leads to low-performance accuracy. Furthermore, traditional segmentation algorithms often require human inputs and cannot be utilized in automated systems. To address all of these issues, we provide an improved segmentation model based on depthwise separable convolutions that act on each spatial dimension of the image to segment the lesions. The fundamental idea behind these convolutions is to divide the feature learning steps into two simpler parts that are spatial learning of features and a step for channel combination. Besides this, we employ parallel multidilated filters to encode multiple parallel features and broaden the view of filters with dilations. Moreover, for performance evaluation, the proposed approach is evaluated on three different datasets including DermIS, DermQuest, and ISIC2016. The finding indicates that the suggested segmentation model has achieved the Dice score of 97% for DermIS and DermQuest and 94.7% for the ISBI2016 dataset, respectively.
Copyright © 2023 Maryam Bukhari et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Efficient skin lesion segmentation using separable-Unet with stochastic weight averaging.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2019 Sep;178:289-301. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2019.07.005. Epub 2019 Jul 8. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2019. PMID: 31416556
-
Digital hair segmentation using hybrid convolutional and recurrent neural networks architecture.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2019 Aug;177:17-30. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2019.05.010. Epub 2019 May 15. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2019. PMID: 31319945
-
An IoMT-Based Melanoma Lesion Segmentation Using Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Mar 28;23(7):3548. doi: 10.3390/s23073548. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37050607 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Learning Approaches Towards Skin Lesion Segmentation and Classification from Dermoscopic Images - A Review.Curr Med Imaging. 2020;16(5):513-533. doi: 10.2174/1573405615666190129120449. Curr Med Imaging. 2020. PMID: 32484086 Review.
-
Melanoma Detection and Classification using Computerized Analysis of Dermoscopic Systems: A Review.Curr Med Imaging. 2020;16(7):794-822. doi: 10.2174/1573405615666191223122401. Curr Med Imaging. 2020. PMID: 33059552 Review.
Cited by
-
Performance Evaluation of Artificial Intelligence Techniques in the Diagnosis of Brain Tumors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cureus. 2025 Jul 28;17(7):e88915. doi: 10.7759/cureus.88915. eCollection 2025 Jul. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40735661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The study on ultrasound image classification using a dual-branch model based on Resnet50 guided by U-net segmentation results.BMC Med Imaging. 2024 Nov 18;24(1):314. doi: 10.1186/s12880-024-01486-z. BMC Med Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39558260 Free PMC article.
-
Melanoma identification and classification model based on fine-tuned convolutional neural network.Digit Health. 2024 May 24;10:20552076241253757. doi: 10.1177/20552076241253757. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Digit Health. 2024. PMID: 38798885 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

