Effect of Phentolamine as Reversal of Soft-Tissue Anesthesia on Post-Endodontic Pain in Patients with Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis: A Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 36794110
- PMCID: PMC9923417
- DOI: 10.22037/iej.v14i2.22452
Effect of Phentolamine as Reversal of Soft-Tissue Anesthesia on Post-Endodontic Pain in Patients with Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Introduction: Phentolamine mesylate (OraVerse) is mostly used to reverse soft tissue anesthesia after dental procedures. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the effect of the injection of OraVerse on postoperative pain after root canal treatment in patients with symptomatic irreversible pulpitis.
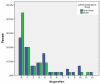
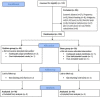
Methods and materials: In this randomized single-blind clinical trial study, 100 patients (50 per group) with symptomatic irreversible pulpitis in the first or second mandibular molars, randomly received either OraVerse or sham treatment after a single-visit root canal therapy. Each patient recorded their pain score, using a Heft Parker visual analogue scale, before and after 6, 12, 24, 36, 48, and 72 h of the treatment. They also monitored their soft-tissue anesthesia every 15 min for 5 h. Data were analyzed by t-test and repeated measured ANOVA statistical tests. The level of significance was set at 0.05.
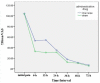
Results: Patients who received phentolamine had significantly higher pain scores at 6- and 12-h postoperative intervals compared with those receiving sham treatment (P=0.01 and P=0.00 respectively). Consumption of analgesics in OraVerse group was significantly higher than that of the sham group (P=0.48).
Conclusion: Although phentolamine accelerated the reversal of normal soft tissue sensation after the dental visit, it increased postoperative pain in patients suffering from symptomatic irreversible pulpitis, which may limit phentolamine administration in this group.
Keywords: Anesthesia; Inferior Alveolar Nerve; Lidocaine; Phentolamine Mesylate; Postoperative Pain.
Conflict of interest statement
‘None declared’.
Figures
References
-
- El Mubarak AH, Abu-bakr NH, Ibrahim YE. Postoperative pain in multiple-visit and single-visit root canal treatment. J Endod. 2010;36(1):36–9. - PubMed
-
- De Oliveira GS Jr, Agarwal D, Benzon HT. Perioperative single dose ketorolac to prevent postoperative pain: a meta-analysis of randomized trials. Anesth Analg. 2012;114(2):424–33. - PubMed
-
- Fernandez C, Reader A, Beck M, Nusstein J. A prospective, randomized, double-blind comparison of bupivacaine and lidocaine for inferior alveolar nerve blocks. J Endod. 2005;31(7):499–503. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
