High expression of FGFR3 predicts a better prognosis for patients with non-small cell lung cancer in a Chinese population
- PMID: 36794128
- PMCID: PMC9922600
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd-22-1523
High expression of FGFR3 predicts a better prognosis for patients with non-small cell lung cancer in a Chinese population
Abstract
Background: This study sought to examine the expression and mutation status of fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) tissues and explore the prognostic potential of FGFR3 in NSCLC.
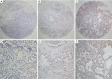
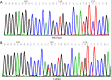
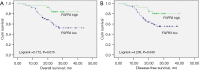
Methods: Immunohistochemistry (IHC) was used to evaluate the FGFR3 protein expression of 116 NSCLC tissues. Sanger sequencing was used to examine the mutation status of exons 7, 10, and 15 in FGFR3. A Kaplan‑Meier survival analysis was conducted to evaluate the association between the expression level of FGFR3 and the overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) of NSCLC patients. Univariate and multivariate Cox analyses were conducted to examine the association between the risk score and clinical features.
Results: FGFR3 was immunoreactive in 26 of the 86 NSCLC cases. Further, FGFR3 was positively expressed in 84.6% of the lung adenocarcinoma (AC) cases and 15.4% of the lung squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) cases. FGFR3 mutations were detected in 2 NSCLC patients (2/72, 2.8%), who both harbored the T450M mutation, a novel mutation in exon 10 of FGFR3. In NSCLC, a high expression of FGFR3 was positively correlated with gender, smoking, histology type, T stage, and the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation (P<0.05). FGFR3 expression was also correlated with better OS and DFS. The multivariate analysis revealed that FGFR3 served as an independent prognostic factor (P=0.024) for the OS of NSCLC patients.
Conclusions: This study showed that FGFR3 was highly expressed in NSCLC tissues, and the frequency rate for the FGFR3 mutation at T450 M in NSCLC tissues was low. The survival analysis suggested that FGFR3 may be a useful prognostic biomarker in NSCLC.
Keywords: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3); immunohistochemistry (IHC); mutation; non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); prognosis.
2023 Journal of Thoracic Disease. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jtd.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jtd-22-1523/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
FGFR1, 2 and 3 protein overexpression and molecular aberrations of FGFR3 in early stage non-small cell lung cancer.J Pathol Clin Res. 2016 Aug 13;2(4):223-233. doi: 10.1002/cjp2.51. eCollection 2016 Oct. J Pathol Clin Res. 2016. PMID: 27785367 Free PMC article.
-
[Correlation Analysis of Ki67 Expression and EGFR Mutation on the Risk of Recurrence and Metastasis in Postoperative Patients with Stage I Lung Adenocarcinoma].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2022 Dec 20;25(12):852-861. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2022.101.55. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 36617471 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Heterogeneous resistance mechanisms in an EGFR exon 19-mutated non-small cell lung cancer patient treated with erlotinib: Persistent FGFR3-mutation, localized transformation to EGFR-mutated SCLC, and acquired T790M EGFR-mutation.Lung Cancer. 2017 Nov;113:14-17. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2017.08.024. Epub 2017 Sep 1. Lung Cancer. 2017. PMID: 29110841
-
Combination of PD-L1 expression and NLR as prognostic marker in patients with surgically resected non-small cell lung cancer.J Cancer. 2019 Oct 22;10(26):6703-6710. doi: 10.7150/jca.34469. eCollection 2019. J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31777599 Free PMC article.
-
Neoadjuvant and adjuvant epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKI) therapy for lung cancer.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2015 Feb;4(1):82-93. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2218-6751.2014.11.08. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25806348 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular Matrix Sulfation in the Tumor Microenvironment Stimulates Cancer Stemness and Invasiveness.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Sep;11(36):e2309966. doi: 10.1002/advs.202309966. Epub 2024 Jul 31. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 39083319 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jonna S, Subramaniam DS. Molecular diagnostics and targeted therapies in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): an update. Discov Med 2019;27:167-70. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
