Allergen-specific immunotherapy with Alutard SQ improves allergic inflammation in house-dust mites-induced allergic asthma rats through inactivation of the HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB pathway
- PMID: 36794148
- PMCID: PMC9922602
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd-22-715
Allergen-specific immunotherapy with Alutard SQ improves allergic inflammation in house-dust mites-induced allergic asthma rats through inactivation of the HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB pathway
Abstract
Background: Allergen-specific immunotherapy (AIT) is the only available safe, effective, and long-term treatment for allergic airway diseases, including allergic asthma. However, the potential molecular mechanism of AIT in ameliorating airway inflammation remains unknown.
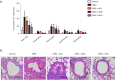
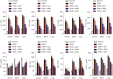
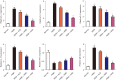
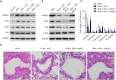
Methods: Rats were sensitized and challenged with house dust mite (HDM) and administered with Alutard SQ or/and high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) inhibitor, ammonium glycyrrhizinate (AMGZ) or HMGB1 lentivirus. The total and differential cell counts in rat bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) were detected. Hematoxylin and eosin staining (H&E) was performed to examine the pathological lesions in lung tissues. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was performed to assess the expression of inflammatory factors in lungs, BALF, and serum. Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) was used to measure the levels of inflammatory factors in the lungs. Western blot assay was used to evaluate the expression of HMGB1, Τoll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), and nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) in the lungs.
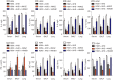
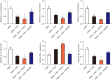
Results: Consequently, AIT with Alutard SQ attenuated airway inflammation, the total and differential cells in BALF, and expression of Th (T helper)2 related cytokines and transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-β1). The regimen also upregulated Th-1-related cytokine expression by inhibiting the HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB pathway in HDM-induced asthmatic rats. Furthermore, AMGZ, a HMGB1 antagonist, amplified the functions of AIT with Alutard SQ in the asthma rat model. Nevertheless, overexpression of HMGB1 reversed the functions of AIT with Alutard SQ in the asthma rat model.
Conclusions: In summary, this work demonstrates the role of AIT with Alutard SQ, which inhibits the HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in allergic asthma management.
Keywords: Asthma; HMGB1/TLR4/NF‐κB pathway; airway inflammation; allergen-specific immunotherapy (AIT) with Alutard SQ; house dust mite.
2023 Journal of Thoracic Disease. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jtd.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jtd-22-715/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Resveratrol protects against asthma-induced airway inflammation and remodeling by inhibiting the HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB pathway.Exp Ther Med. 2019 Jul;18(1):459-466. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.7594. Epub 2019 May 20. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 31258683 Free PMC article.
-
Methods for Experimental Allergen Immunotherapy: Subcutaneous and Sublingual Desensitization in Mouse Models of Allergic Asthma.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2223:295-335. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1001-5_20. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33226602
-
Subcutaneous and Sublingual Immunotherapy in a Mouse Model of Allergic Asthma.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1559:137-168. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6786-5_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28063043
-
New perspectives in allergen specific immunotherapy driven by big trials with house dust mite sublingual SQ® tablets.Clin Mol Allergy. 2020 Jun 11;18:10. doi: 10.1186/s12948-020-00124-7. eCollection 2020. Clin Mol Allergy. 2020. PMID: 32536827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
House dust mite subcutaneous immunotherapy in Chinese patients with allergic asthma and rhinitis.J Thorac Dis. 2019 Aug;11(8):3616-3625. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2019.06.35. J Thorac Dis. 2019. PMID: 31559069 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
[Effects of iris xanthin on airway inflammation, airway remodeling, and the HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB pathway in asthmatic young mice].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2024 Jun 15;26(6):639-645. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2312023. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38926382 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Molecular Study from the Signaling Pathways of Four Potential asthma triggers: AKT1, MAPK13, STAT1, and TLR4.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 28;26(13):6240. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136240. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40650018 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
