Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi affect the expression of PxNHX gene family, improve photosynthesis and promote Populus simonii× P. nigra growth under saline-alkali stress
- PMID: 36794207
- PMCID: PMC9923091
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1104095
Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi affect the expression of PxNHX gene family, improve photosynthesis and promote Populus simonii× P. nigra growth under saline-alkali stress
Abstract
Introduction: Saline-alkali stress seriously endangers the normal growth of Populus simonii×P. nigra. Arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi can enhance the saline-alkali tolerance of plants by establishing a symbiotic relationship with them.
Methods: In this study, a pot experiment was conducted to simulate a saline-alkali environment where Populus simonii×P. nigra were inoculated with Funneliformis mosseae to explore their effects on the saline-alkali tolerance of Populus simonii×P. nigra.
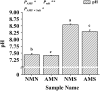
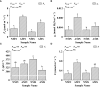
Results and discussion: Our results show that a total of 8 NHX gene family members are identified in Populus simonii×P. nigra. F. mosseae regulate the distribution of Na+ by inducing the expression of PxNHXs. The pH value of poplar rhizosphere soil is reduced, result in the promote absorption of Na+ by poplar, that ultimately improved the soil environment. Under saline-alkali stress, F. mosseae improve the chlorophyll fluorescence and photosynthetic parameters of poplar, promote the absorption of water, K+ and Ca2+, thus increase the plant height and fresh weight of aboveground parts, and promote the growth of poplar. Our results provide a theoretical basis for further exploring the application of AM fungi to improve the saline-alkali tolerance of plants.
Keywords: Funneliformis mosseae; NHX gene family; Populus simonii×P. nigra; arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi; saline-alkali stress.
Copyright © 2023 Dong, Wang, Tao, Xu and Tang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Abbaspour H., Pour F. S. N., Abdel-Wahhab M. A. (2021). Arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis regulates the physiological responses, ion distribution and relevant gene expression to trigger salt stress tolerance in pistachio. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 27 (8), 1765–1778. doi: 10.1007/s12298-021-01043-w - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arab Y., Marjan, Shahsavani S., Akhyani A., Dorostkar V. (2018). Pomegranate growth affected by arbuscular mycorrhizae, phosphorus fertilizer, and irrigation water aalinity. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 49 (4), 478–488. doi: 10.1080/00103624.2018.1431265 - DOI
-
- Athar H., Zafar Z. U., Ashraf M. (2015). Glycinebetaine improved photosynthesis in canola under salt stress: evaluation of chlorophyll fluorescence parameters as potential indicators. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 201 (6), 428–442. doi: 10.1111/jac.12120 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

