Vitamins A, C, and E Exert Anti-apoptotic Function in the Testis of Rats After Exposure to Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles
- PMID: 36794239
- PMCID: PMC9900230
- DOI: 10.4068/cmj.2023.59.1.48
Vitamins A, C, and E Exert Anti-apoptotic Function in the Testis of Rats After Exposure to Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles
Abstract
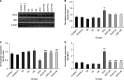
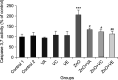
Some reports emphasize that zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) are detrimental to the reproductive organs of animals. As such, this research aimed at exploring the apoptotic potential of ZnO NPs on testis along with the beneficial role of Vitamins (V) A, C, and E against ZnO NP-induced damage. To this aim, a population of 54 healthy, male Wistar rats were used in this work and then assigned into nine groups of 6 rats as G1: Control 1 (Water); G2: Control 2 (Olive oil); G3: VA (1000 IU/kg), G4: VC (200 mg/kg), G5: VE (100 IU/kg), G6: ZnO NPs exposed animals (200 mg/kg); and G7, 8 and 9: ZnO NPs-exposed animals that were pre-treated with either VA, C, or E. Apoptosis rates were estimated by measuring the level of apoptotic regulatory markers including Bcl-2-associated X (Bax) and B-cell lymphoma protein 2 (Bcl-2) using western blotting and qRT-PCR assays. The data indicated that ZnO NPs exposure elevates the level of Bax protein and gene expression, whereas the protein and gene expression of Bcl-2 was reduced. Further, the activation of caspase-3,7 occurred after exposure to ZnO NPs, while the above alterations were significantly alleviated in the rats that were co-treated with VA, C, or E and ZnO NPs relative to the rats in the ZnO NPs group. In summary, VA, C, and E exerted anti-apoptotic functions in the testis of rats following administration of ZnO NPs.
Keywords: Antioxidants; Apoptosis; Nanoparticles; Rats; Zinc Oxide.
© Chonnam Medical Journal, 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT: None declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The antioxidant and anti-apoptotic properties of vitamins A, C and E in heart tissue of rats exposed to zinc oxide nanoparticles.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Mar;50(3):2357-2365. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-08103-8. Epub 2022 Dec 29. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 36580195
-
The Alleviative Efficacy of Vitamins A, C, and E Against Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles-Induced Hepatic Damage by Reducing Apoptosis in Rats.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2023 Mar;201(3):1252-1260. doi: 10.1007/s12011-022-03218-2. Epub 2022 Apr 1. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2023. PMID: 35364806
-
Protective effects of green and chemical zinc oxide nanoparticles on testis histology, sperm parameters, oxidative stress markers and androgen production in rats treated with cisplatin.Cell Tissue Res. 2021 May;384(2):561-575. doi: 10.1007/s00441-020-03350-2. Epub 2021 Jan 12. Cell Tissue Res. 2021. PMID: 33433689
-
Ameliorative Effects of Vitamins A, C, and E on Sperm Parameters, Testis Histopathology, and Oxidative Stress Status in Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle-Treated Rats.Biomed Res Int. 2023 Jan 17;2023:4371611. doi: 10.1155/2023/4371611. eCollection 2023. Biomed Res Int. 2023. PMID: 36704721 Free PMC article.
-
The protective effects of vitamins A, C, and E on zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs)-induced liver oxidative stress in male Wistar rats.Drug Chem Toxicol. 2023 Mar;46(2):209-218. doi: 10.1080/01480545.2021.2016809. Epub 2021 Dec 16. Drug Chem Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 34915775
Cited by
-
Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Induced Testicular Toxicity Through Inflammation and Reducing Testosterone and Cell Viability in Adult Male Rats.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025 Apr;203(4):1934-1948. doi: 10.1007/s12011-024-04330-1. Epub 2024 Aug 12. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025. PMID: 39134772 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kuang H, Yang P, Yang L, Aguilar ZP, Xu H. Size dependent effect of ZnO nanoparticles on endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling pathway in murine liver. J Hazard Mater. 2016;317:119–126. - PubMed
-
- Fan P, Yang C, Wang L, Wang Q, Zhang Y, Zhou J, et al. ZnO nanoparticles stimulate oxidative stress to induce apoptosis of B16F10 melanoma cells: in vitro and in vivo studies. Biomed Phys Eng Express. 2021;7:065014 - PubMed
-
- Chen H, Luo L, Fan S, Xiong Y, Ling Y, Peng S. Zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized from Aspergillus terreus induces oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis through modulating apoptotic proteins in human cervical cancer HeLa cells. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2021;73:221–232. - PubMed
-
- Kuang H, Zhang W, Yang L, Aguilar ZP, Xu H. Reproductive organ dysfunction and gene expression after orally administration of ZnO nanoparticles in murine. Environ Toxicol. 2021;36:550–561. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

