Adverse renal effects associated with cardiopulmonary bypass
- PMID: 36794518
- PMCID: PMC10943608
- DOI: 10.1177/02676591231157055
Adverse renal effects associated with cardiopulmonary bypass
Abstract
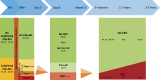
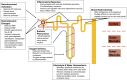
Cardiac surgery on cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) is associated with postoperative renal dysfunction, one of the most common complications of this surgical cohort. Acute kidney injury (AKI) is associated with increased short-term morbidity and mortality and has been the focus of much research. There is increasing recognition of the role of AKI as the key pathophysiological state leading to the disease entities acute and chronic kidney disease (AKD and CKD). In this narrative review, we will consider the epidemiology of renal dysfunction after cardiac surgery on CPB and the clinical manifestations across the spectrum of disease. We will discuss the transition between different states of injury and dysfunction, and, importantly, the relevance to clinicians. The specific facets of kidney injury on extracorporeal circulation will be described and the current evidence evaluated for the use of perfusion-based techniques to reduce the incidence and mitigate the complications of renal dysfunction after cardiac surgery.
Keywords: bypass; cardiac; injury; kidney; surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

