Genetic variants and haplotypes in fibulin-5 (FBLN5) are associated with pseudoexfoliation glaucoma but not with pseudoexfoliation syndrome
- PMID: 36794549
- PMCID: PMC9995586
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20221622
Genetic variants and haplotypes in fibulin-5 (FBLN5) are associated with pseudoexfoliation glaucoma but not with pseudoexfoliation syndrome
Abstract
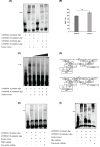
Pseudoexfoliation (PEX) is a multifactorial age-related disease involving deposition of extracellular proteinaceous aggregates on anterior ocular tissues. The present study aims to identify functional variants in fibulin-5 (FBLN5) as risk factors for the development of PEX. Thirteen tag single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in FBLN5 were genotyped using TaqMan SNP genotyping technology to identify association between SNPs of FBLN5 and PEX in an Indian cohort comprising 200 control and 273 PEX patients (169 PEXS and 104 PEXG). Functional analysis of risk variants was done through luciferase reporter assays and electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) using human lens epithelial cells. Genetic association and risk haplotype analysis showed a significant association of rs17732466:G>A (NC_000014.9:g.91913280G>A) and rs72705342:C>T (NC_000014.9:g.91890855C>T) within FBLN5 as risk factors with the advanced severe stage of the disease, pseudoexfoliation glaucoma (PEXG). Reporter assays showed allele-specific regulatory effect of rs72705342:C>T on gene expression, wherein, construct containing the risk allele showed a significant decrease in the reporter activity compared with the one with protective allele. EMSA further validated higher binding affinity of the risk variant to nuclear protein. In silico analysis predicted binding sites for two transcription factors, GR-α and TFII-I with risk allele at rs72705342:C>T, which were lost in the presence of protective allele. The EMSA showed probable binding of both these proteins to rs72705342. In conclusion, the present study identified the novel association of two genetic variants in FBLN5 with PEXG but not with PEXS, distinguishing between the early and the later forms of PEX. Further, rs72705342:C>T was found to be a functional variant.
Keywords: fibulin-5; functional variant; pseudoexfoliation glaucoma; tag genotyping.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures


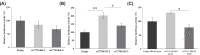
Similar articles
-
De novo variants in an extracellular matrix protein coding gene, fibulin-5 (FBLN5) are associated with pseudoexfoliation.Eur J Hum Genet. 2019 Dec;27(12):1858-1866. doi: 10.1038/s41431-019-0482-6. Epub 2019 Jul 29. Eur J Hum Genet. 2019. PMID: 31358954 Free PMC article.
-
Susceptibility to pseudoexfoliation linked to intronic variant rs4926246 in CACNA1A: Evidence from an Indian population study.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2025 Mar;1868(1):195076. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2025.195076. Epub 2025 Jan 16. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2025. PMID: 39826673
-
Association of lysyl oxidase-like 1 gene common sequence variants in Greek patients with pseudoexfoliation syndrome and pseudoexfoliation glaucoma.Mol Vis. 2013 Jul 12;19:1446-52. Print 2013. Mol Vis. 2013. PMID: 23869164 Free PMC article.
-
Current understanding of genetics and epigenetics in pseudoexfoliation syndrome and glaucoma.Mol Aspects Med. 2023 Dec;94:101214. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2023.101214. Epub 2023 Sep 18. Mol Aspects Med. 2023. PMID: 37729850 Review.
-
Is pseudoexfoliation glaucoma a neurodegenerative disorder?J Biosci. 2021;46:97. J Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34785624 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

