Preclinical assessment of the feasibility, safety and lesion durability of a novel 'single-shot' pulsed field ablation catheter for pulmonary vein isolation
- PMID: 36794699
- PMCID: PMC10105880
- DOI: 10.1093/europace/euad030
Preclinical assessment of the feasibility, safety and lesion durability of a novel 'single-shot' pulsed field ablation catheter for pulmonary vein isolation
Abstract
Aims: Single-shot pulmonary vein isolation can improve procedural efficiency. To assess the capability of a novel, expandable lattice-shaped catheter to rapidly isolate thoracic veins using pulsed field ablation (PFA) in healthy swine.
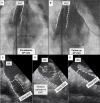
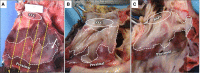
Methods and results: The study catheter (SpherePVI; Affera Inc) was used to isolate thoracic veins in two cohorts of swine survived for 1 and 5 weeks. In Experiment 1, an initial dose (PULSE2) was used to isolate the superior vena cava (SVC) and the right superior pulmonary vein (RSPV) in six swine and the SVC only in two swine. In Experiment 2, a final dose (PULSE3) was used for SVC, RSPV, and left superior pulmonary vein (LSPV) in five swine. Baseline and follow-up maps, ostial diameters, and phrenic nerve were assessed. Pulsed field ablation was delivered atop the oesophagus in three swine. All tissues were submitted for pathology. In Experiment 1, all 14/14 veins were isolated acutely with durable isolation demonstrated in 6/6 RSPVs and 6/8 SVC. Both reconnections occurred when only one application/vein was used. Fifty-two and 32 sections from the RSPVs and SVC revealed transmural lesions in 100% with a mean depth of 4.0 ± 2.0 mm. In Experiment 2, 15/15 veins were isolated acutely with 14/15 veins (5/5 SVC, 5/5 RSPV, and 4/5 LSPV) durably isolated. Right superior pulmonary vein (31) and SVC (34) sections had 100% transmural, circumferential ablation with minimal inflammation. Viable vessels and nerves were noted without evidence of venous stenosis, phrenic palsy, or oesophageal injury.
Conclusion: This novel expandable lattice PFA catheter can achieve durable isolation with transmurality and safety.
Keywords: Atrial fibrillation; Catheter ablation; Electroporation • Oesophageal injury; Pulmonary vein; Single shot.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Drs Koruth and Reddy have received research grants from Affera, Inc. Drs Koruth and Reddy also hold stock options in Affera, Inc. A comprehensive list of other financial disclosures unrelated to this manuscript is included in Supplement. All other authors have no conflicts of interest relevant to this study.
Figures






References
-
- Koruth JS, Kuroki K, Kawamura I, Stoffregen WC, Dukkipati SR, Neuzil Pet al. Focal pulsed field ablation for pulmonary vein isolation and linear atrial lesions: a preclinical assessment of safety and durability. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 2020;13:e008716. - PubMed
-
- Stewart MT, Haines DE, Verma A, Kirchhof N, Barka N, Grassl Eet al. Intracardiac pulsed field ablation: proof of feasibility in a chronic porcine model. Heart Rhythm 2019;16:754–64. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

