The covalent nucleotide modifications within plant mRNAs: What we know, how we find them, and what should be done in the future
- PMID: 36794718
- PMCID: PMC10226571
- DOI: 10.1093/plcell/koad044
The covalent nucleotide modifications within plant mRNAs: What we know, how we find them, and what should be done in the future
Abstract
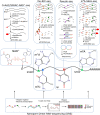
Although covalent nucleotide modifications were first identified on the bases of transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), a number of these epitranscriptome marks have also been found to occur on the bases of messenger RNAs (mRNAs). These covalent mRNA features have been demonstrated to have various and significant effects on the processing (e.g. splicing, polyadenylation, etc.) and functionality (e.g. translation, transport, etc.) of these protein-encoding molecules. Here, we focus our attention on the current understanding of the collection of covalent nucleotide modifications known to occur on mRNAs in plants, how they are detected and studied, and the most outstanding future questions of each of these important epitranscriptomic regulatory signals.
© American Society of Plant Biologists 2023. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement. The authors declare no conflicts of interest related to this work.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

